Other Objects

stellar evolution
NASA/Chandra
Exo-Planets
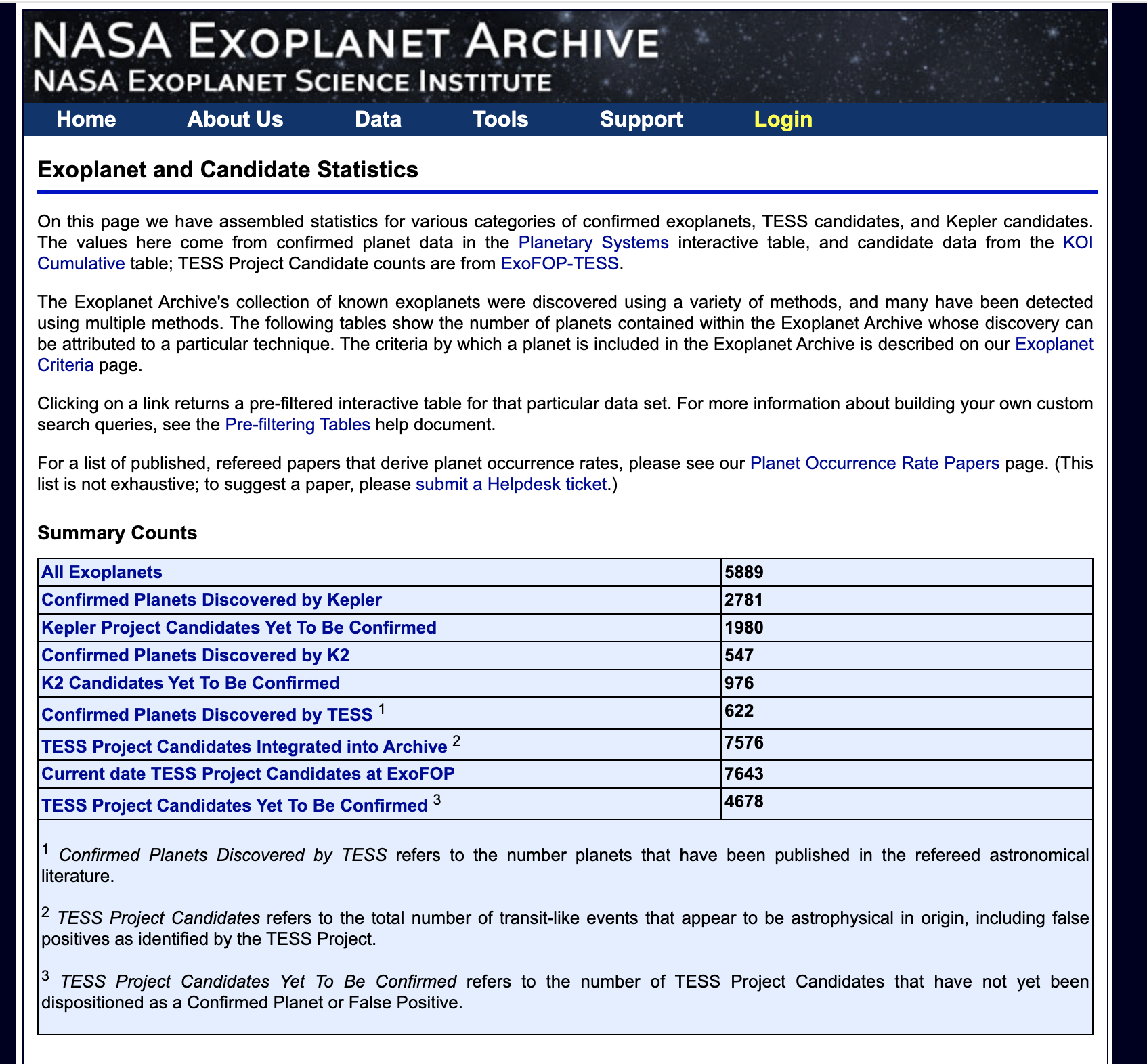
Current Count
https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/docs/counts_detail.html
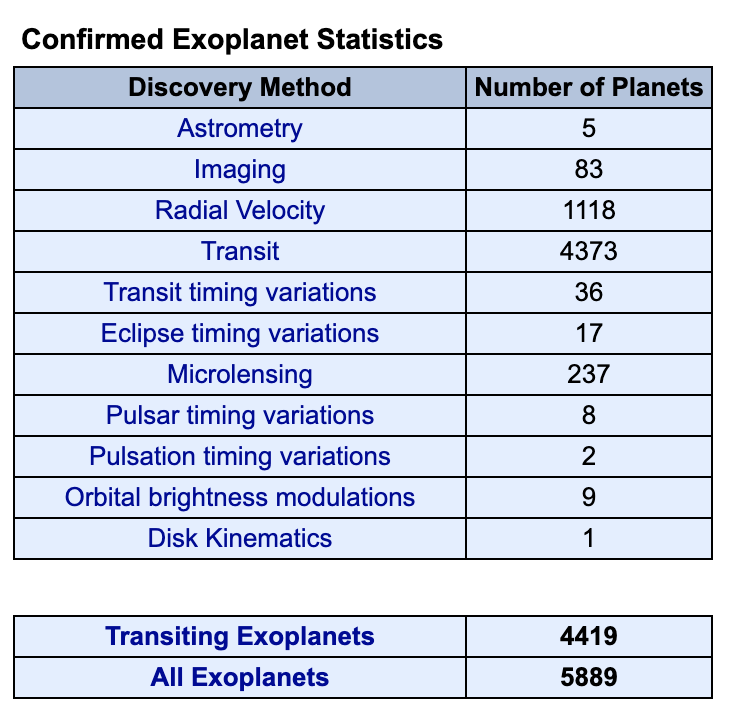
Current Count
https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/docs/counts_detail.html
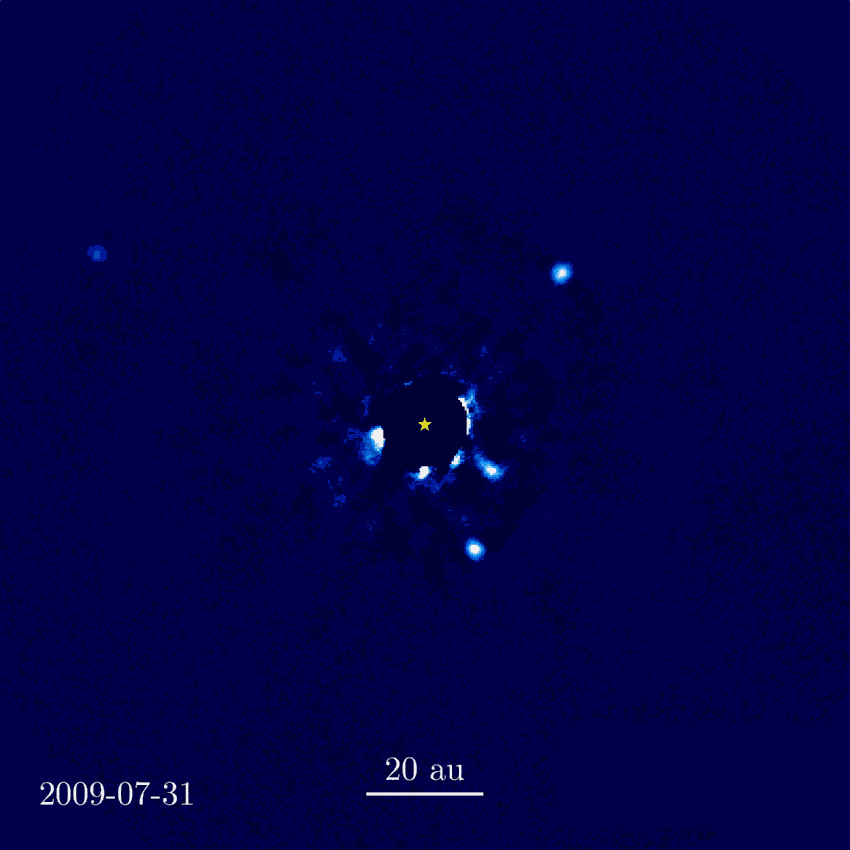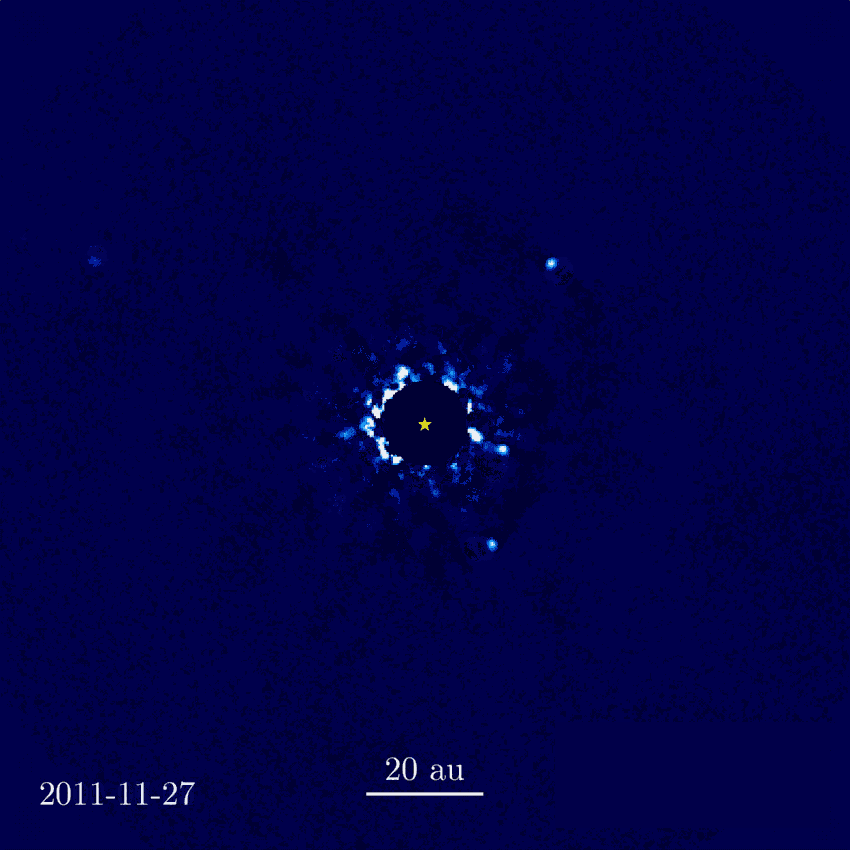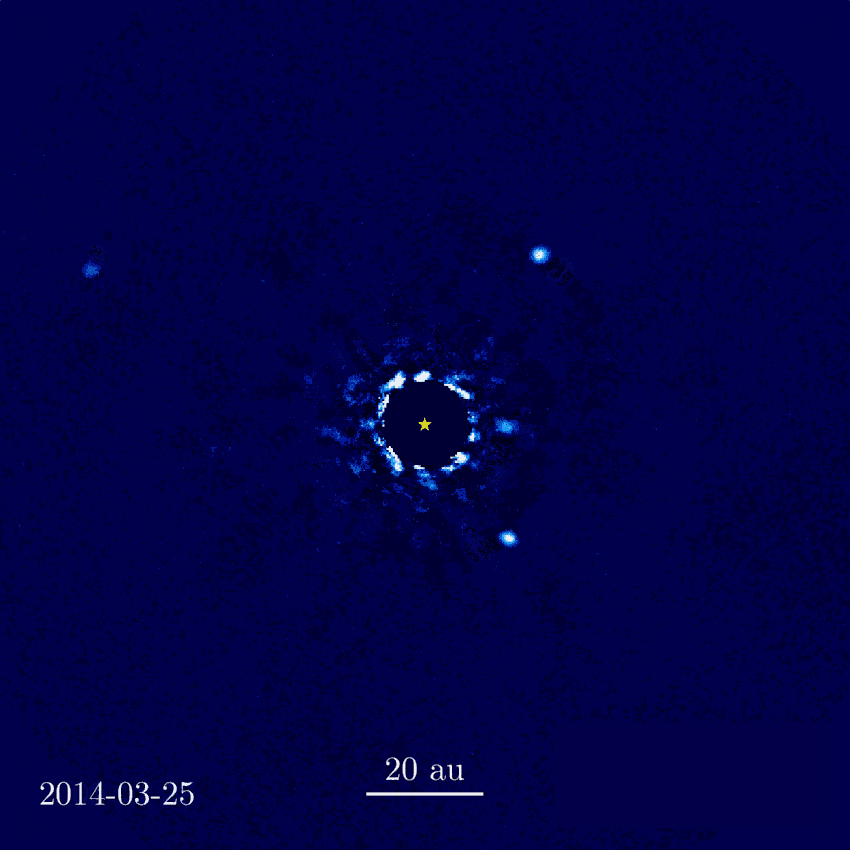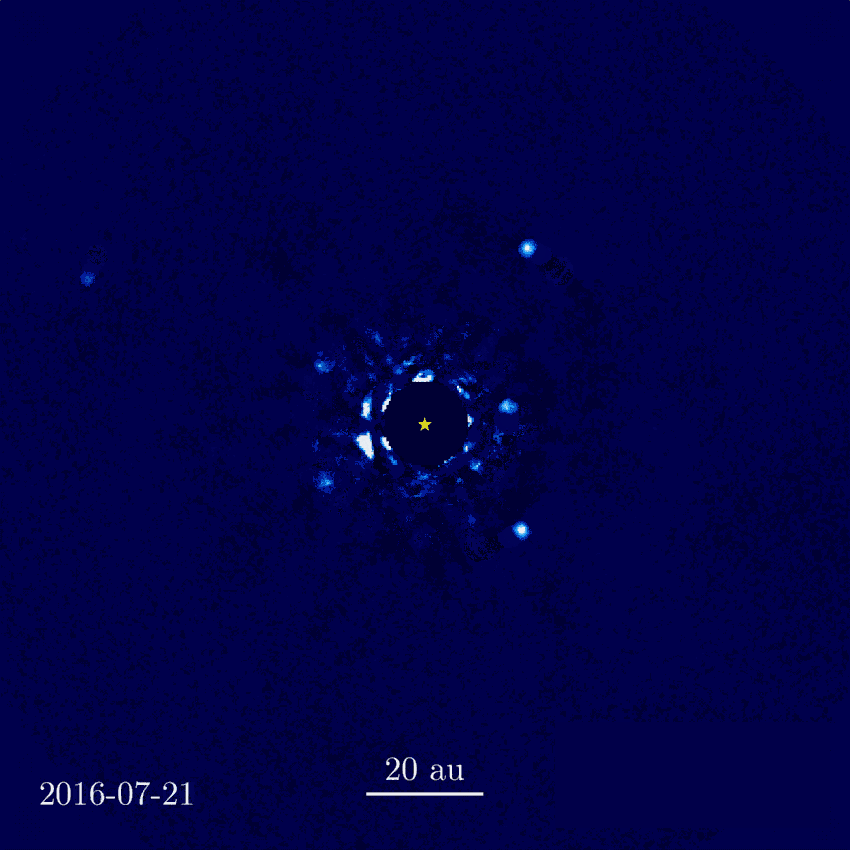
HR 8799 (center)
from W. M. Keck Observatory
First direct imaging of an expolanet system orbiting

HR 8799 - revisited by JWST
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, W. Balmer (JHU), L. Pueyo (STScI), M. Perrin (STScI)
First direct imaging of an expolanet system orbiting
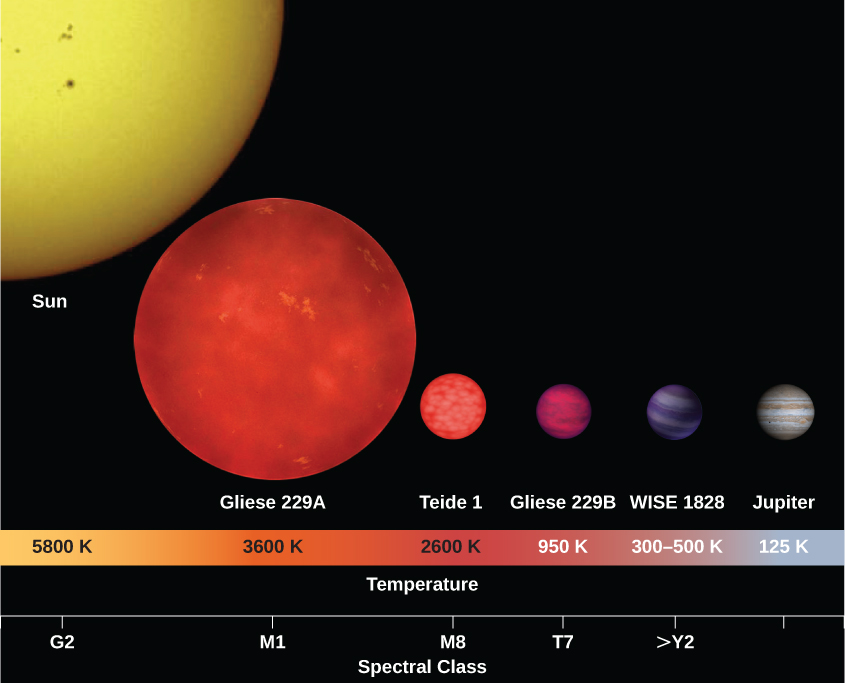
Brown Dwarf
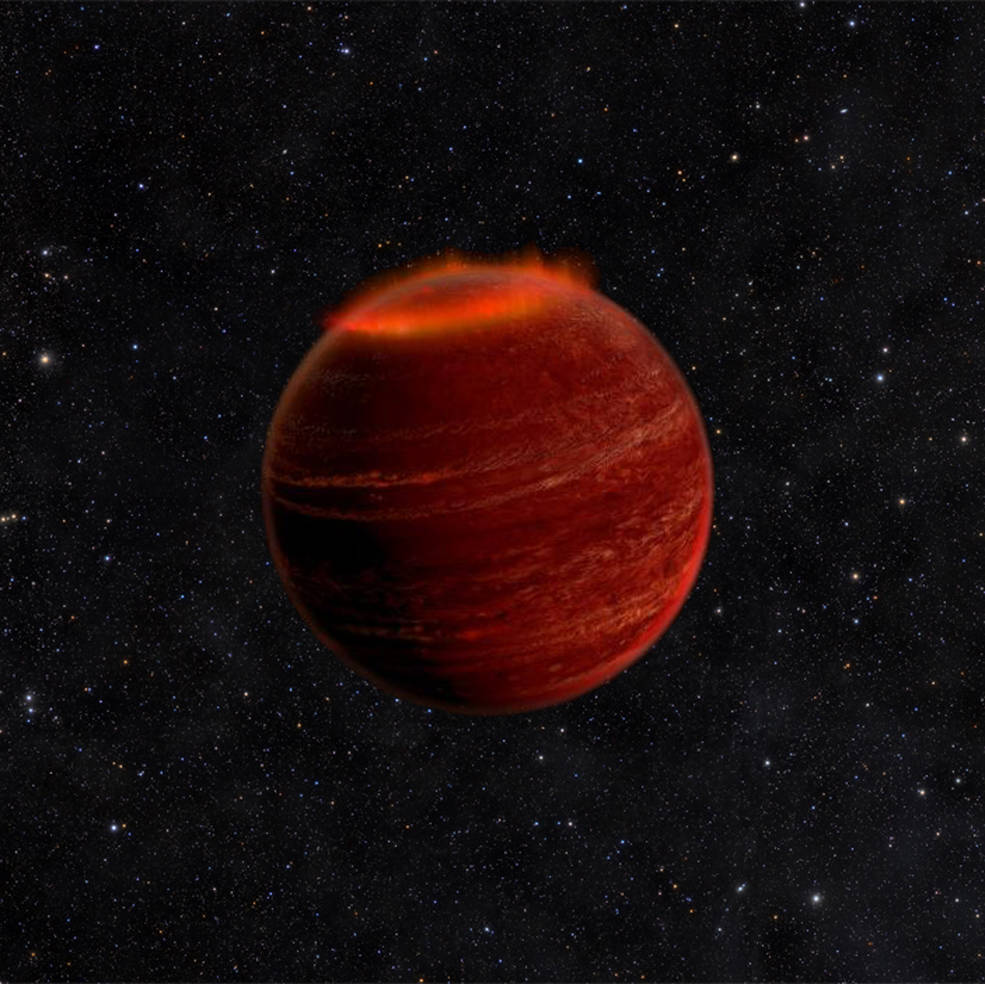

A Brown Dwarf - too small to be a star, too big to be a planet
Chuck Carter and Gregg Hallinan/Caltech
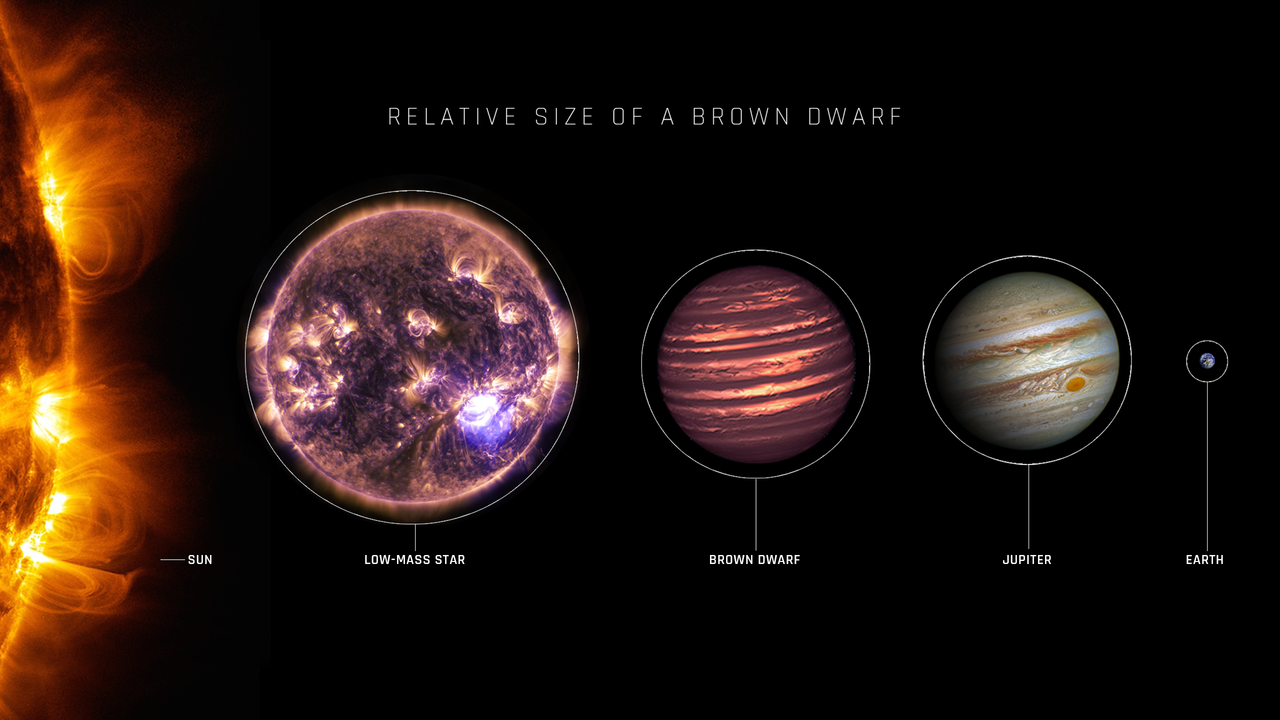

NASA, ESA, SDO, NASA-JPL, Caltech, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC) / https://webbtelescope.org/contents/media/images/4196-Image
Spectra
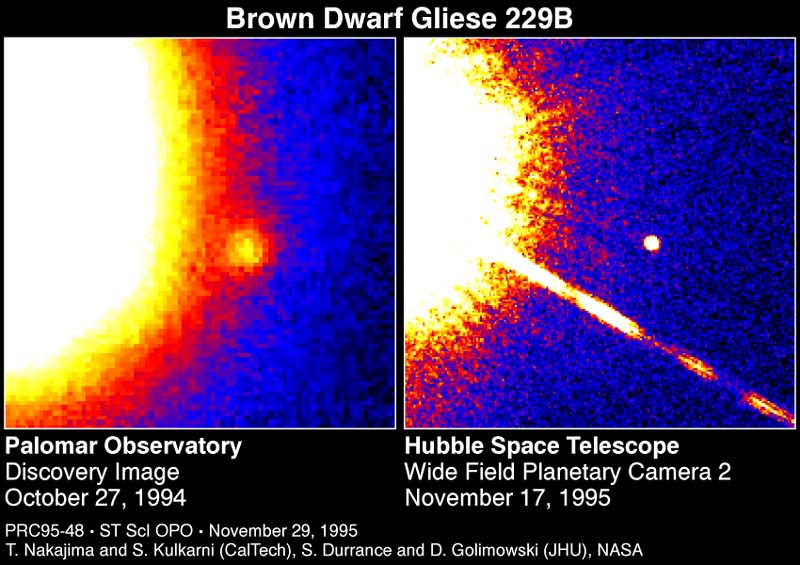
https://science.nasa.gov/asset/hubble/brown-dwarf-discovered-around-star-gliese-229/
Two Brown Dwarfs in tight orbits
Credits: K. Miller, R. Hurt (Caltech/IPAC) https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/its-twins-mystery-of-famed-brown-dwarf-solved
Our Sun

White Dwarf
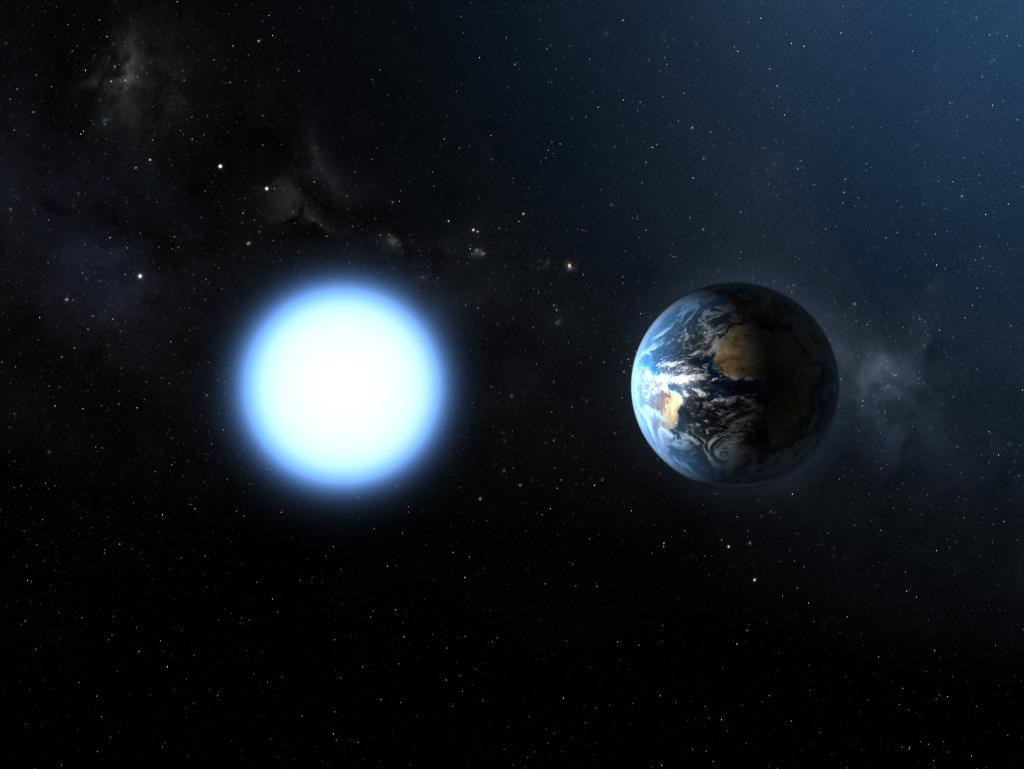

A white dwarf compared to Earth
ESA and NASA
The end of the road for stars like our sun.
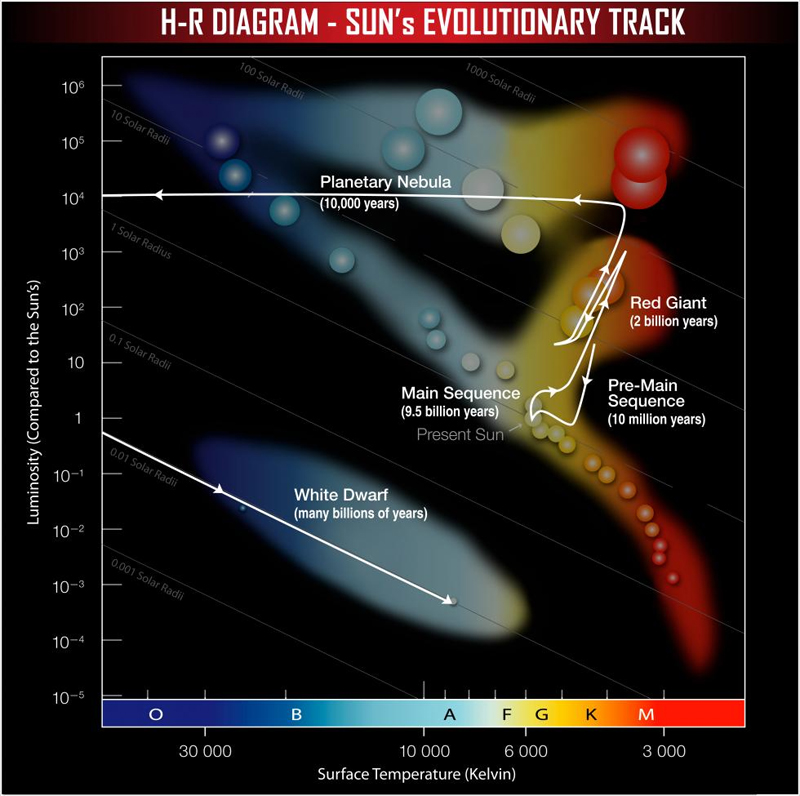
https://chandra.harvard.edu/edu/formal/variable_stars/bg_info.html
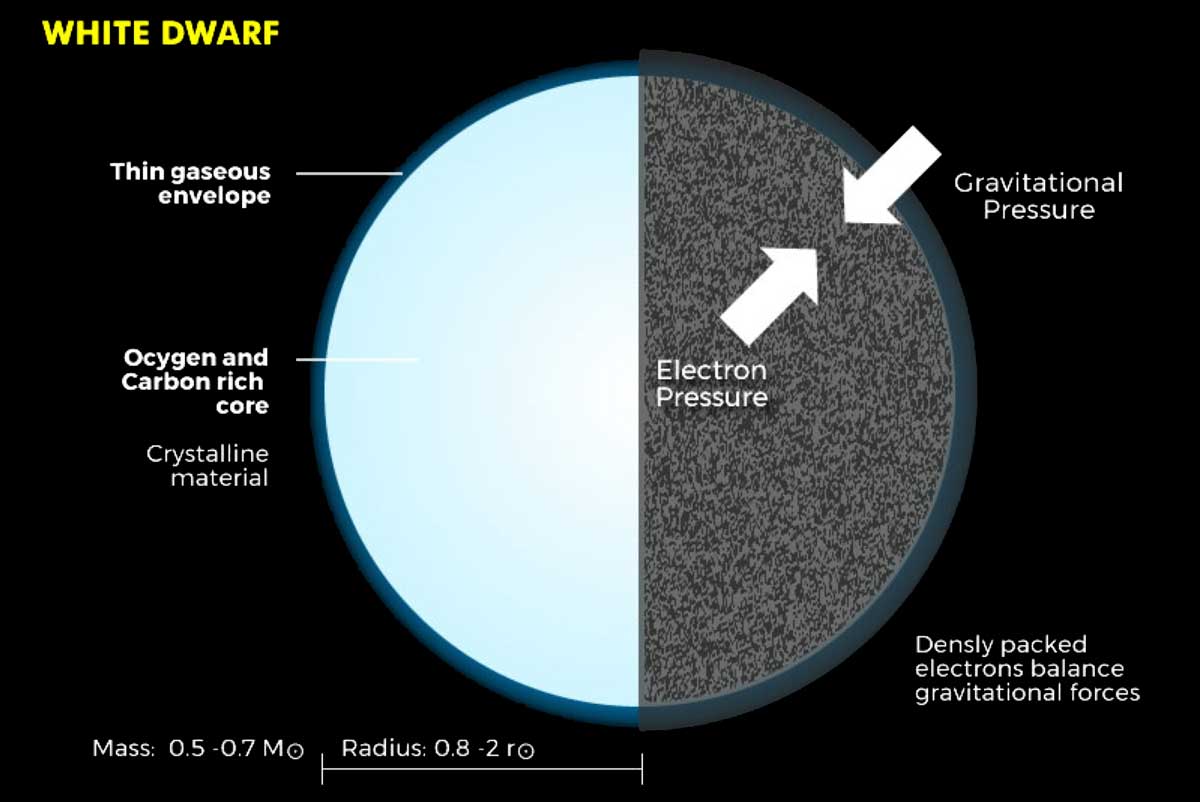
Quantum Mechanics:
- Pauli Exclusion: No duplicate quantum states.
- Heisenberg Uncertainty: $\Delta x \Delta p_x \approx \hbar$
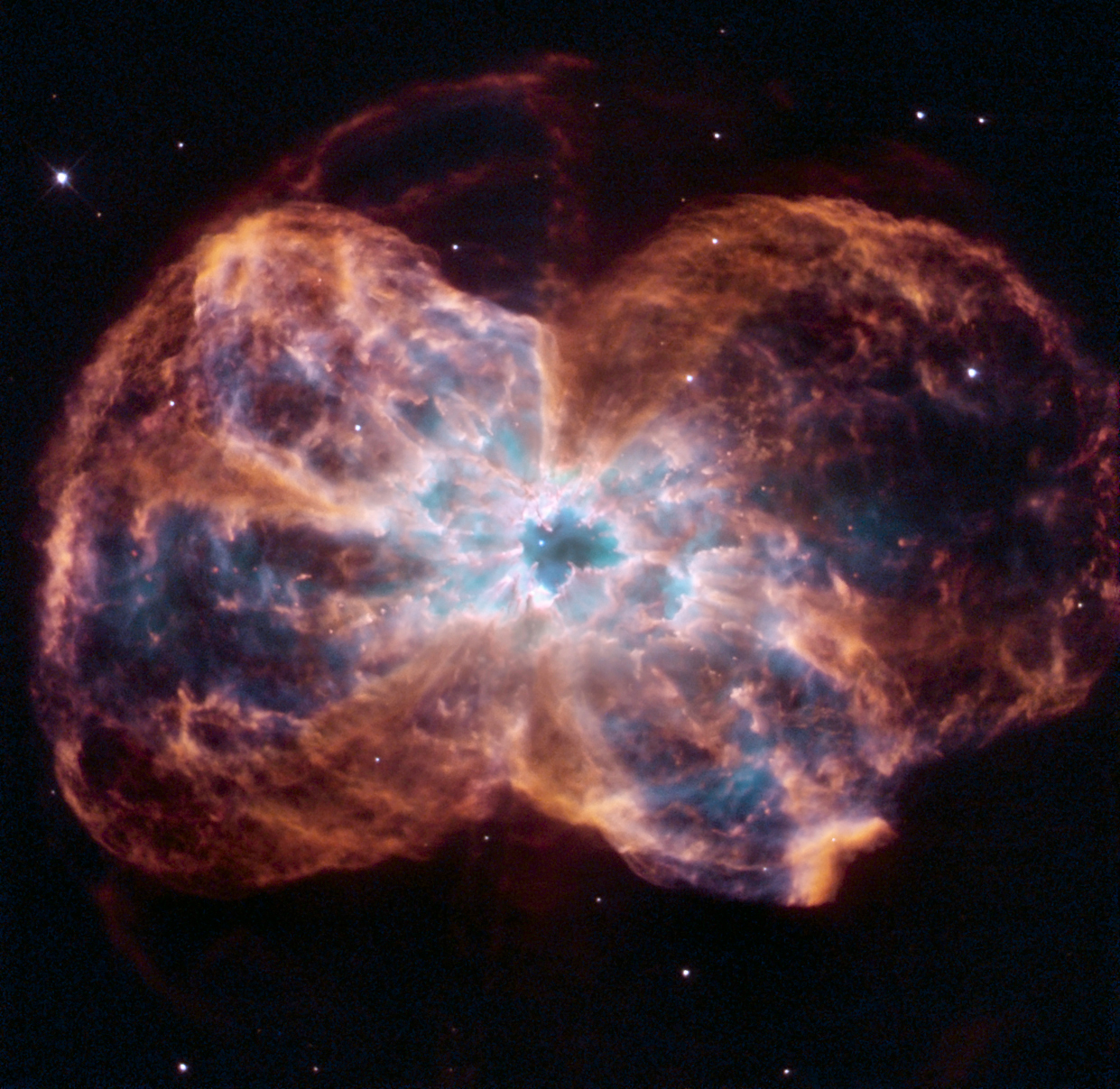

NGC 2440, by Hubble.
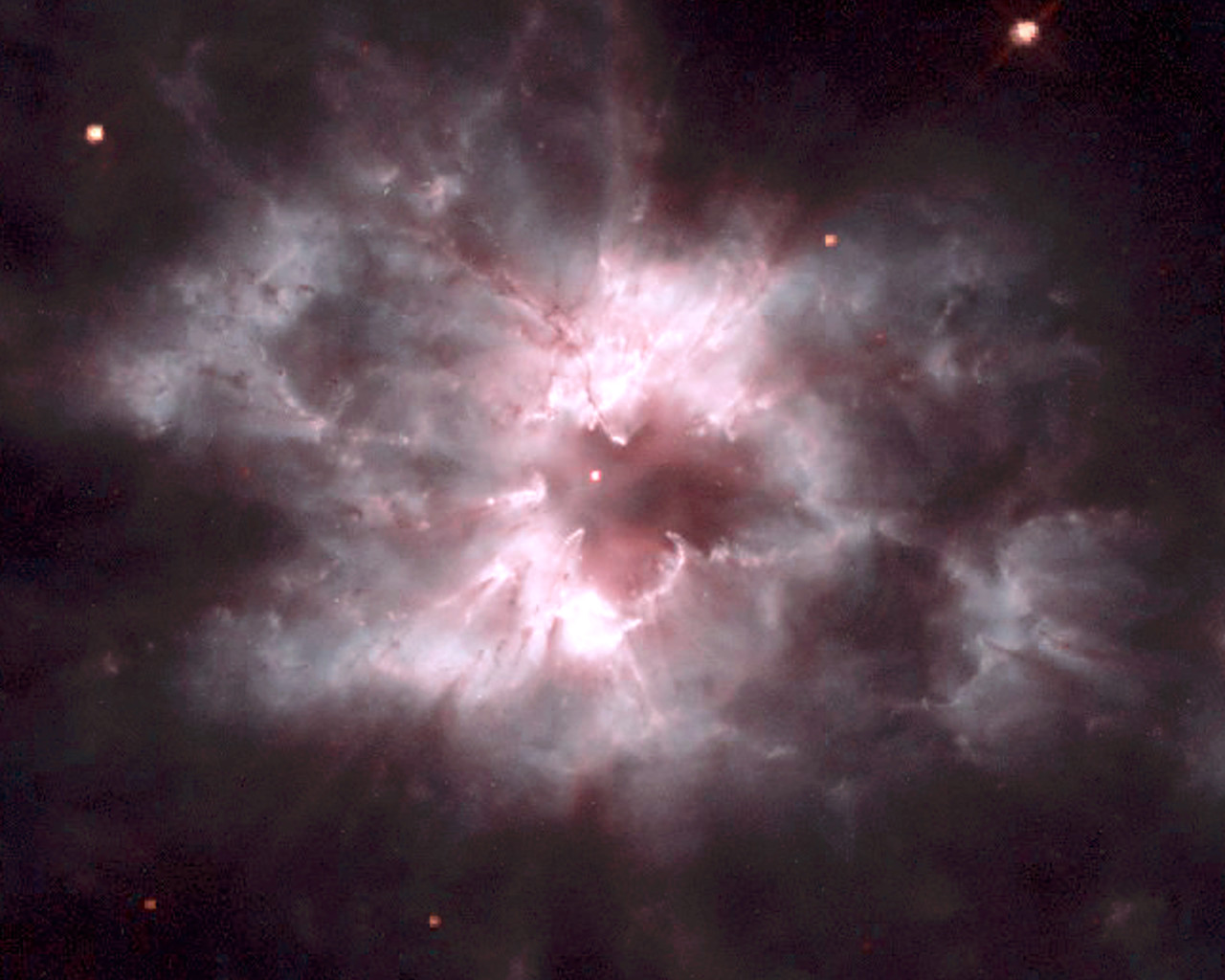

Close up.
Betelgeuse
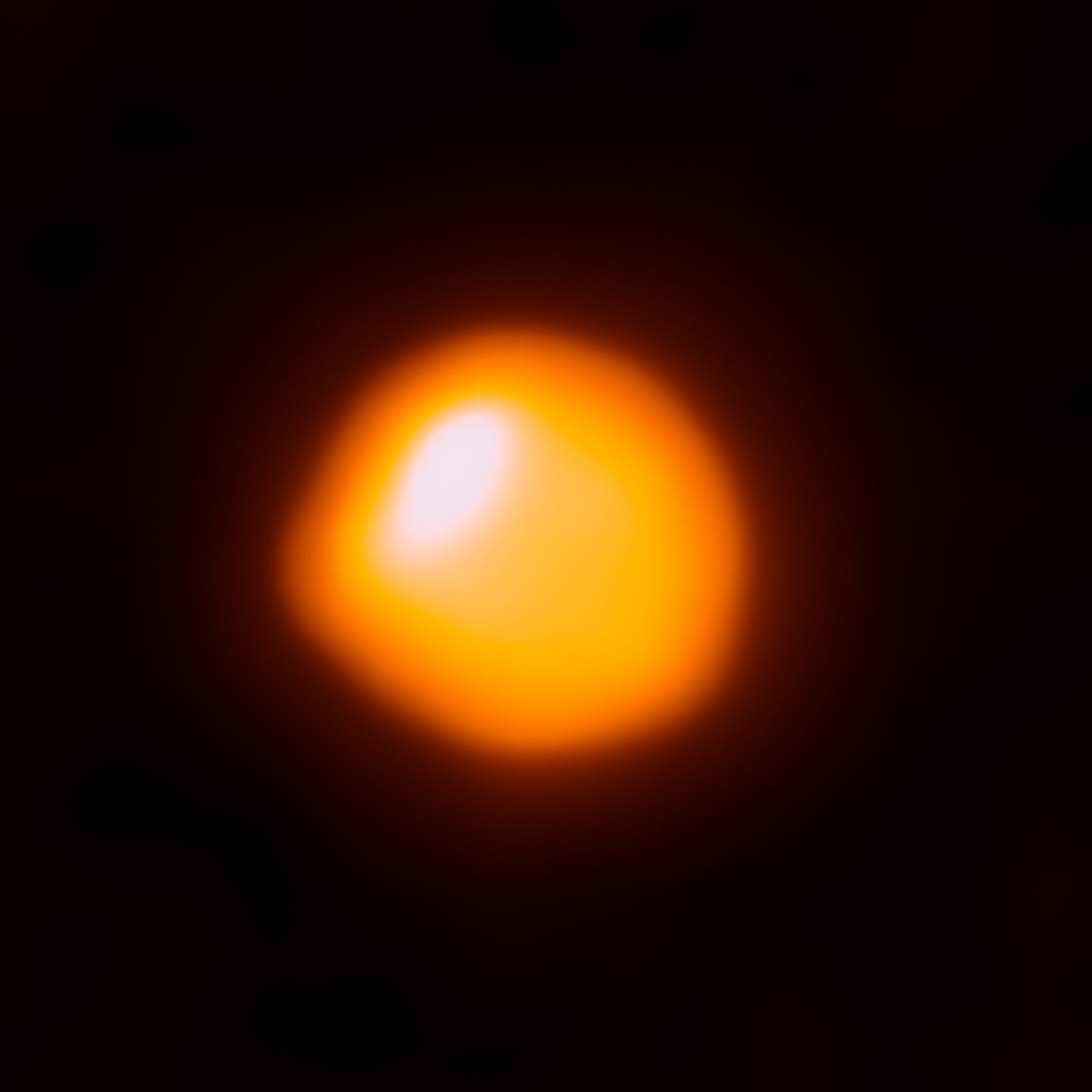

Betelgeuse, as seen by the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
Supernovae
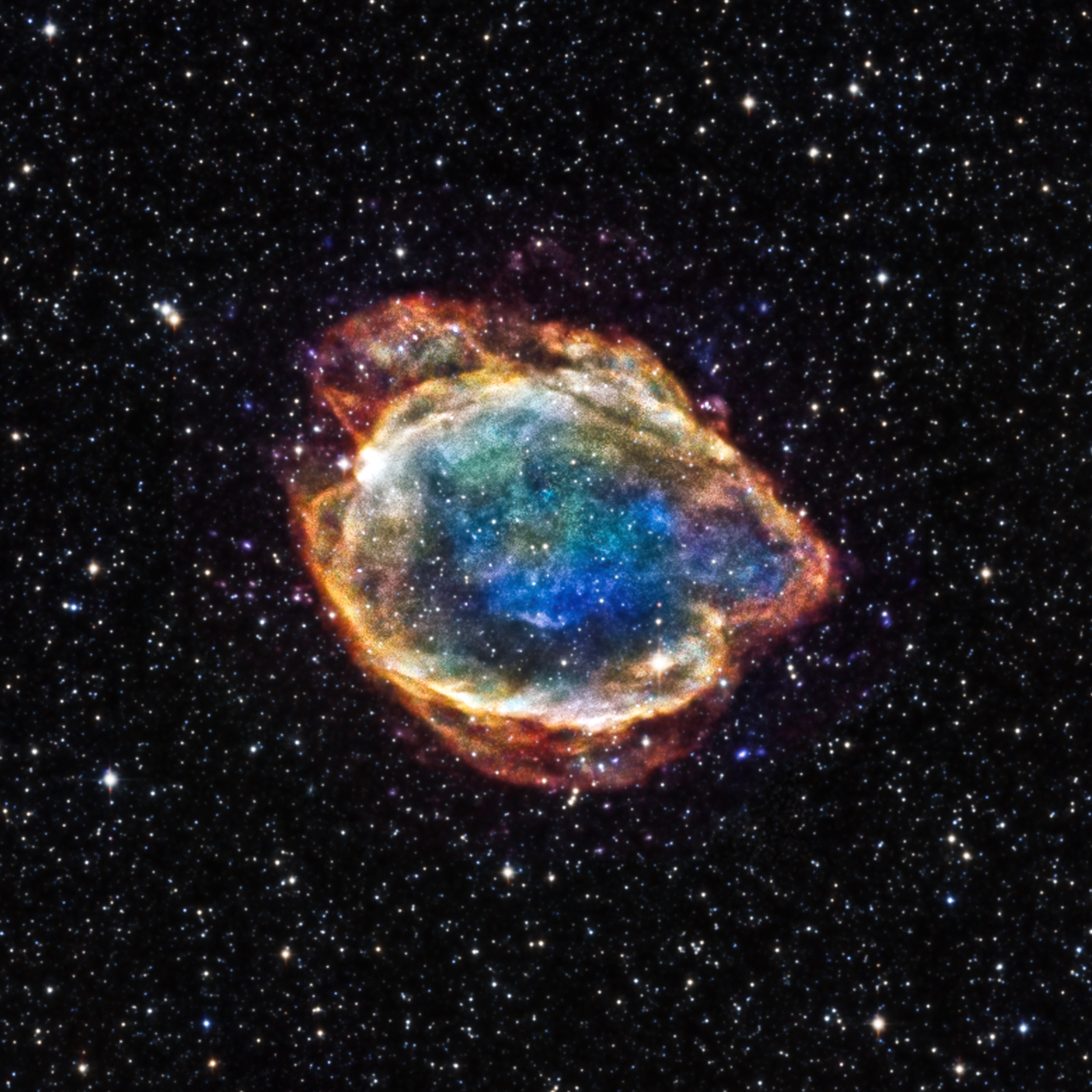

The supernova remnant called G299.2-2.9 (or G299 for short) is located within our Milky Way galaxy

NASA/ESA/HEIC and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
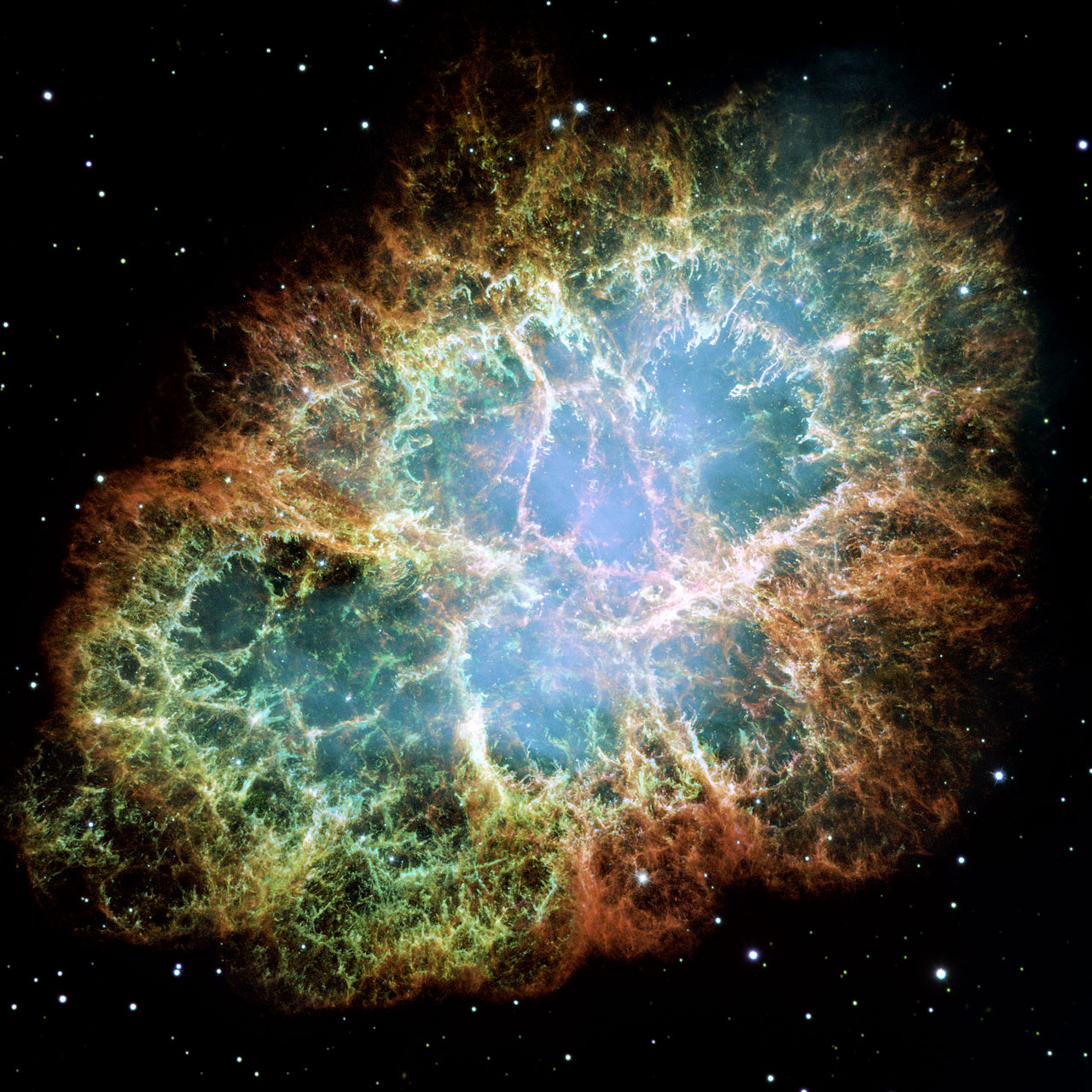

The crab nebula is a supernova remnant in the constellation of Taurus 1054 C.E
NASA, ESA and Allison Loll/Jeff Hester (Arizona State University). Acknowledgement: Davide De Martin (ESA/Hubble)
Neutron Stars
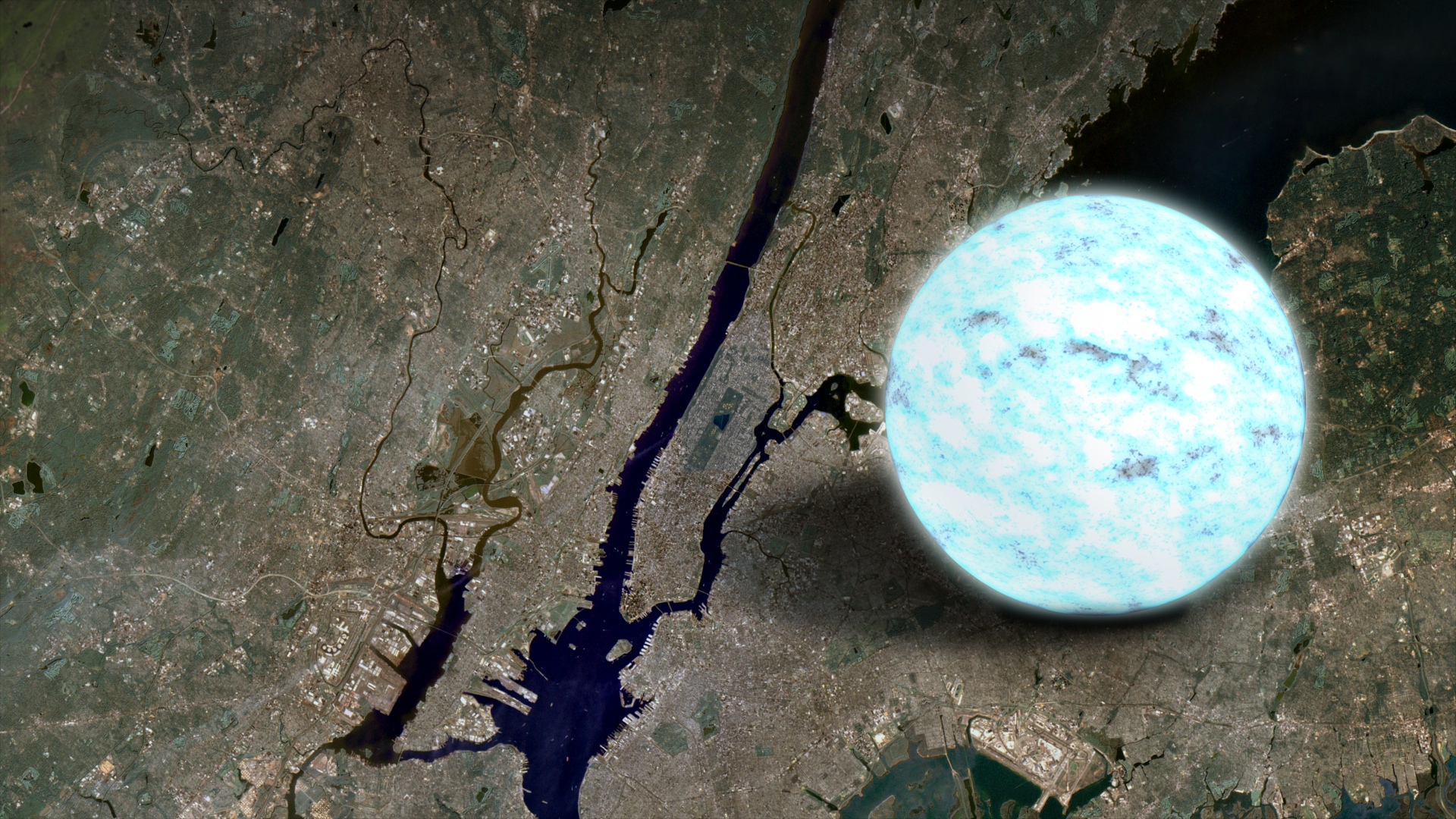

A neutron star is the crushed core of a massive star that ran out of fuel, collapsed under its own weight, and exploded as a supernova
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Pulsars

Jocelyn Bell first observed a pulsar in 1967
what-is-a-pulsar
NASA Goddard, Public Domain
Pulsars used to tell everyone where we are.
Black Holes
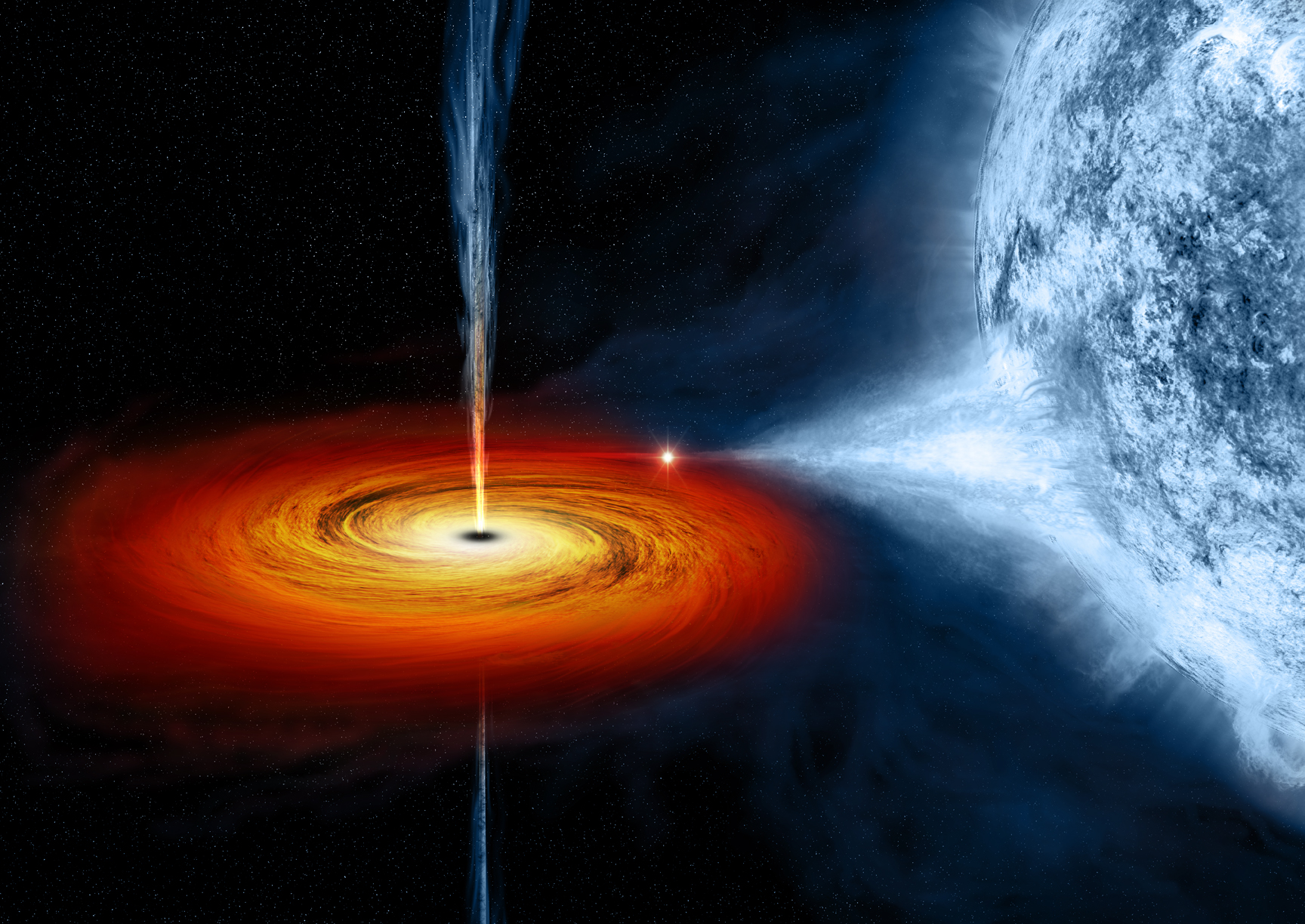

An artist's drawing a black hole named Cygnus X-1. It formed when a large star caved in. This black hole pulls matter from blue star beside it.
Credits: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss

By NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) - HubbleSite: gallery, release., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=102873
Quasars
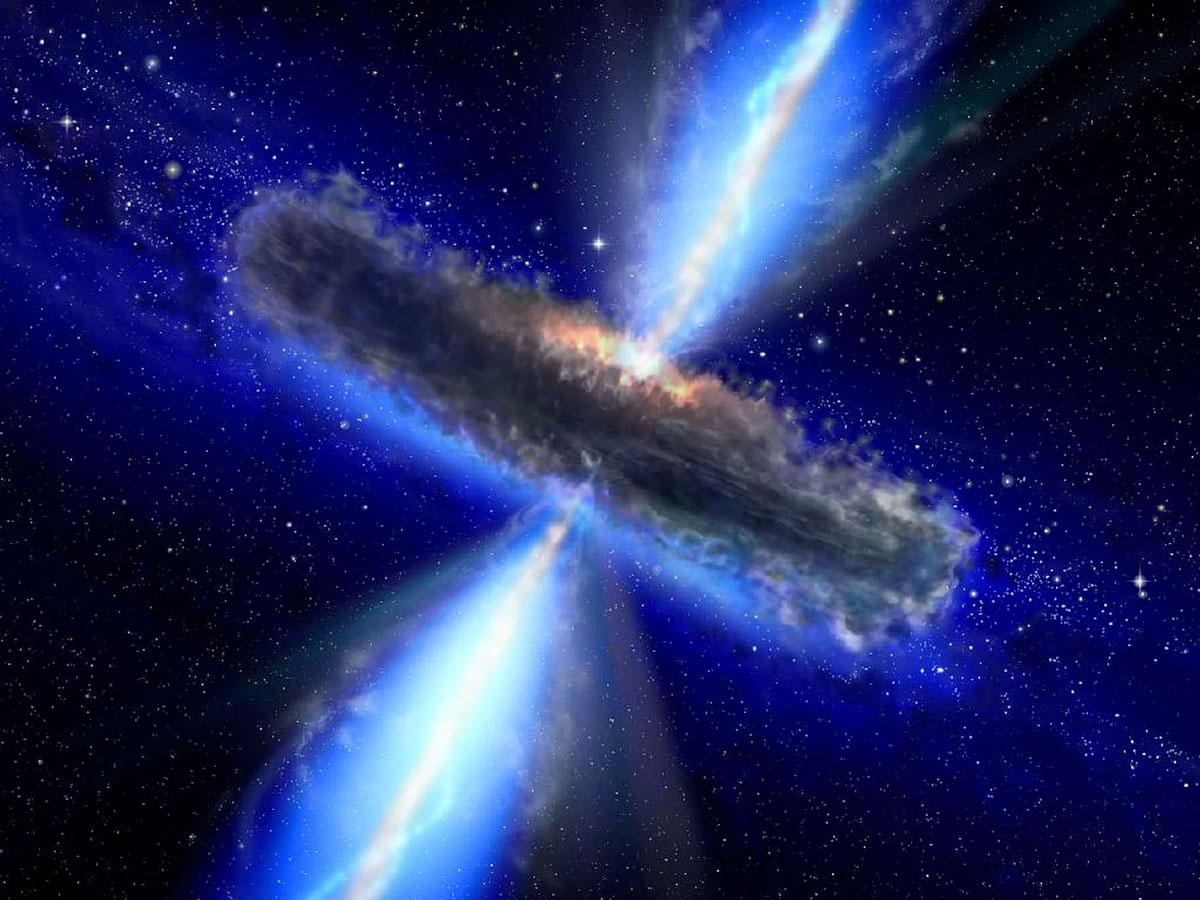

This artist's concept illustrates a quasar, or feeding black hole, similar to APM 08279+5255, where astronomers discovered huge amounts of water vapor. Gas and dust likely form a torus around the central black hole, with clouds of charged gas above and below.
Credit: NASA/ESA


Lensing
https://webbtelescope.org/contents/media/images/2022/035/01G7DCWB7137MYJ05CSH1Q5Z1Z
Cosmology Simulations
Cosmology Simulation/p>
TNG Simulations


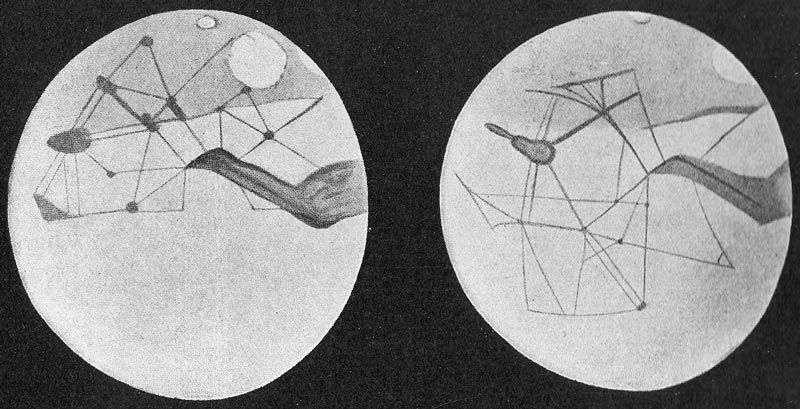
Mars canals illustrated by astronomer Percival Lowell, 1898
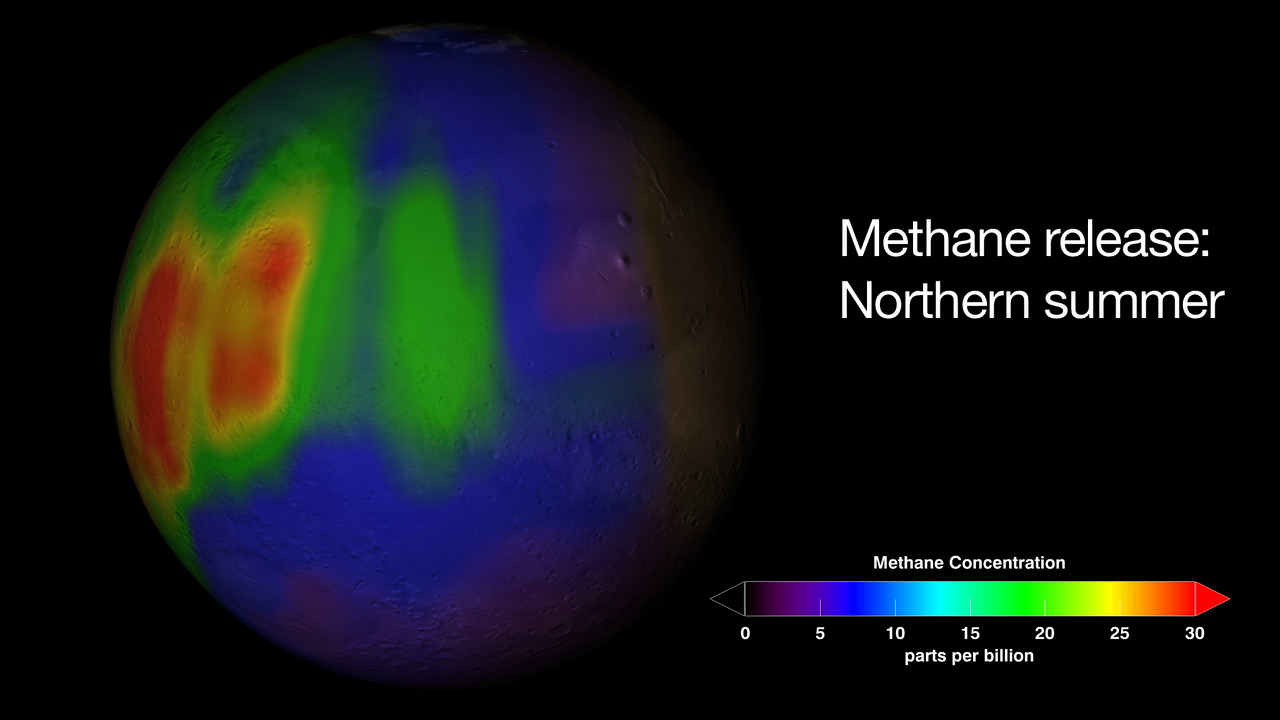
Visualization of a methane plume found in Mars’ atmosphere during the northern summer season.
Credit: Trent Schindler/NASA
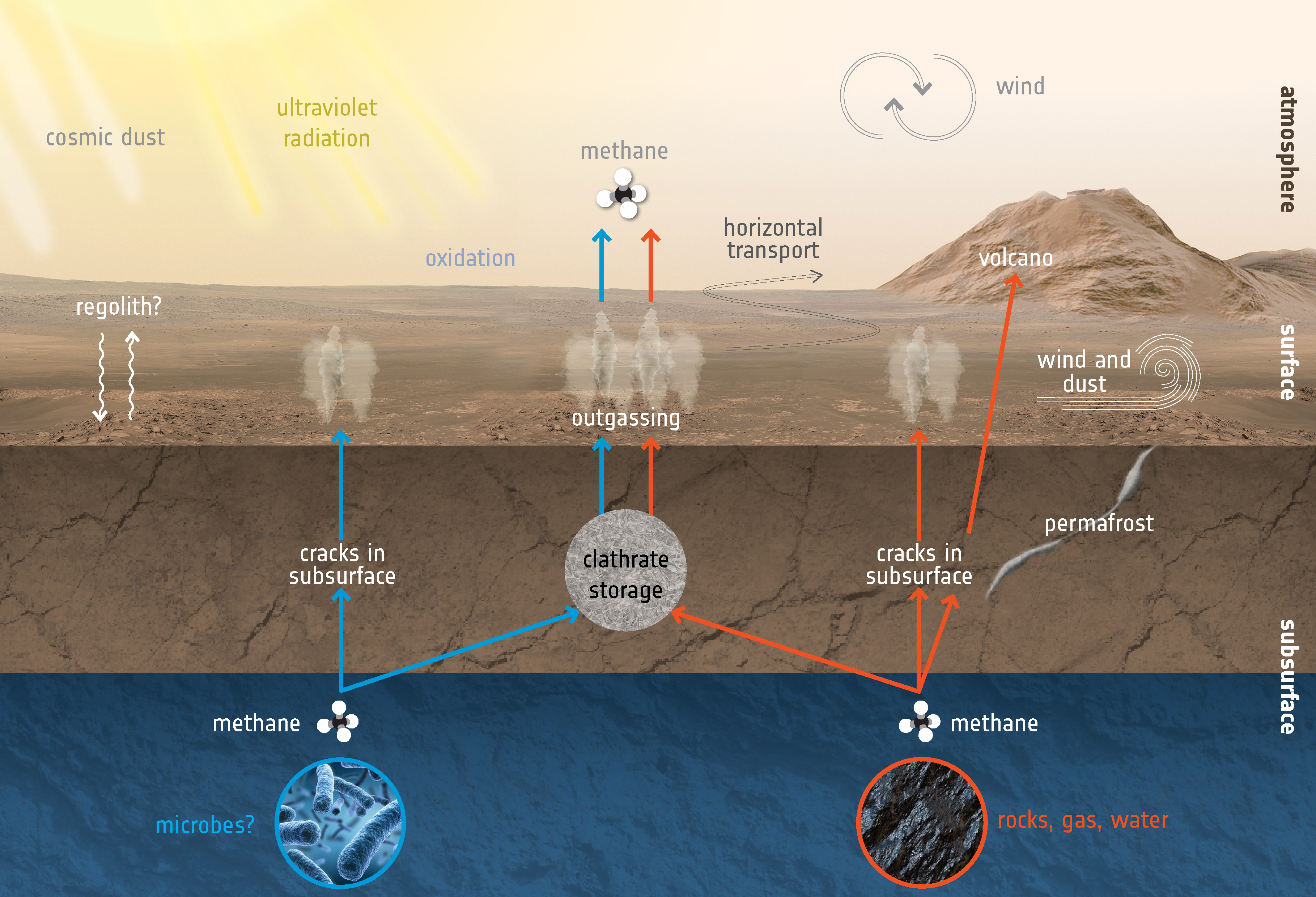
Methane Mystery
https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Exploration/ExoMars/The_methane_mystery
Fermi Paradox

Enrico Fermi, 1901-1954
Given that there are a lot of stars out there, why don't we see any signs of other life?