The Ptolemaic system
Title: Pioneers of Science https://www.gutenberg.org/files/28613/28613-h/28613-h.htm
Much has been written about the history of our understanding of the universe, in particular regarding the position of the earth with respect to the other celestial bodies. Briefly, early astronomers (or natural philosophers) relied on religious principles to create their world views. Western religious traditions considered man to be very important, thus the earth was located at the center, and was stationary. This model fit not only with the religious contexts, but since it is very hard to see the effects of the earth's rotation in other ways besides looking at the stars, seemed to fit well with observations. Aristotle's work provided the basis for many systems of the world. Since church edit demanded that any cosmology be aligned with Aristotle's teachings, western science was forced to work with the following constraints:
the earth was at the center of the universe and was to remain motionless,
everything moves around the earth,
celestial bodies are divine and must move in perfect circles.
These views were adopted by western religions and any deviations from them were considered to be against the religious order: i.e. bad, and punishable. So, astronomers built systems of the world that adhered to these principles. For many years, things were fine. Consider the most basic observations: that once a day, both the Sun and the Stars seem to move around the earth. This is completely explainable by having the sun and the stars move around the earth, once a day, on a diurnal motion.
Claudius Ptolemy
Representation of Ptolemy
Par Andre Thevet angoumoysin, premier cosmographe du roy., premier tome, livre II, chap. 41, "Claude Ptolemee Pelusien", p. 87. Published by Blanche Marantin and Guillaume Chaudiere, Paris, 1584.
Claudius Ptolemy was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer who lived under Roman rule in Egypt. There were also many people named 'Ptolemy' in the ruling dynasty of ancient Egypt. The astronomer was not one of these rulers.
Ptolemy's Arrangement
Starting with the a stationary earth, Ptolemy had to build a system that would account for as many of the observed phenomena of the celestial bodies. The most basic was the diurnal motion of everything. Once every 24 hours, the stars, sun, moon and planets would appear to travel all the way around the earth. Explaining this could be done simply by having their respective celestial spheres rotate once every 24 hours. This explained diurnal motion. (We should note that what counted as an explanation 2000 years ago would probably not carry much weight today.)
Next, one obvious thing people could see was the change in the sun's path through the sky over the course of the year. In summer, the sun was high in the sky at noon. During the winter, it was lower. To explain this, Ptolemy would just need to add another motion to the sun's sphere. Done. (again, no one felt compelled to really probe the obvious follow-up question: why does this sphere do this?)
Retrograde Motion
(stellarium demo)
It didn't take too long for the careful observers of the night sky to realize that sometimes, the planets would appear to move backwards in their tracks along the stars. If you took note of the note of position of Mars at the same time every night, over the course of several months, you would observe its motion to at times be in the same direction as the fixed stars, and at other times, it would appear to be moving in the opposite direction as the stars. This feature became known as retrograde motion. The planet appears to move backwards. What could possibly explain that?
Epicycles
A basic epicycle scheme showing the earth (at center), the deferent, and a planet on its epicycle.
Celestial bodies had to move in circular paths because they were divine and circles were the most perfect shape. One way to explain the retrograde motion of the planets was to add a second circle on which the planet actually orbited. This second circle, called an epicycle, would be carried around the earth by a larger circle, known as the deferent. With careful adjustments of the diameters of the deferent and epicycle, as well as their respective angular velocities, Ptolemy was able to predict with decent accuracy the observed retrograde motion. This structure, the deferent/epicycle, became the hallmark of the Ptolemaic system.
Equants
The equant is an offset from the deferent's center around which the epicycle will move with constant angular velocity.
Another tool to 'save the appearances' was the equant. It permitted Ptolemy to explain why planets moved faster sometime and slower other times, which still moving in uniform circular motion. The earth (or center of the universe) was offset from the center of the deferent, and the the epicycle was said to move in regular circular motion around a third point, the equant, on the other side of the deferent center from the earth. The result was when the planet was closer to the earth, it moved faster, when farther away, it would move across the sky slower.
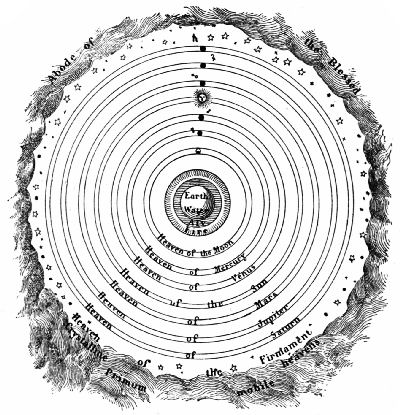
Ptolemaic System
We can't feel the motion of the earth.
Humans are the best, and therefore should be at the center.
No stellar parallax was observed.
Regarding point 1: At the equator, the surface of the earth is moving at about 460 meters per second. Surely, we should be able to feel this, right? Consider the acceleration due to gravity: roughly 9.8 m/s2 . The rotation of the earth would lead to an accelertion towards its center given by: $a_c = \frac{v^2}{R_E}$, where $R_E$ is the radius of the earth: about 6371 kilometers. The give a centripetal acceleration of approximately 0.033 m/s2 . Which is about 1/3 of a percent the acceleration due to gravity. If you remember measuring little g in the first year labs, you should recall it was difficult to get a very precise measurement, even using modern technology. Thus, it would be very hard to measure such a change several thousand years ago.
Regarding Point 2: The universe doesn't owe us any favors. Justifying physical laws based on our supposed greatness is never a good idea. (we know that now)
Regarding Point 3: Parallax was hard to measure and it even took a century or two after the telescope was invented to measure it accurately, so it's hard to blame them back then!
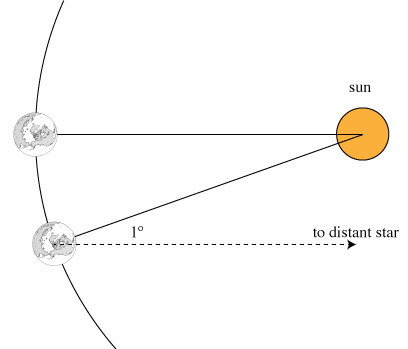
Parallax
The relative position of near and far stars would appear to change if the earth was in motion due to parallax
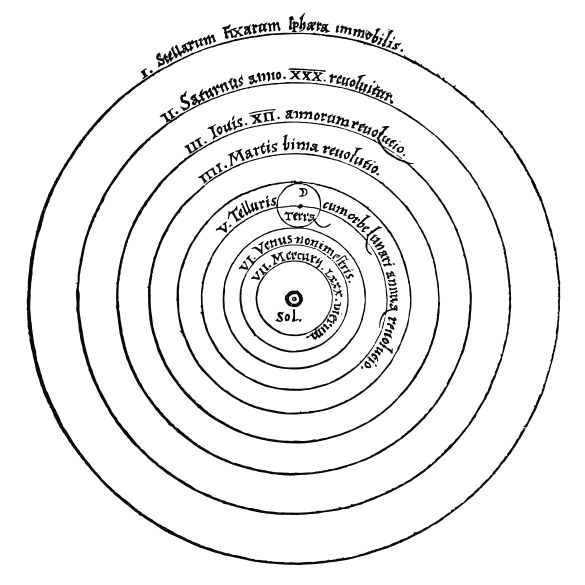
Heliocentric
From De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), 1543. The copernican world view gets an illustration
While not the first to suggest it, Nicolaus Copernicus was the first to provide a compelling argument for the heliocentric model of the solar system. He was hesitant to release his manuscript however, and it did not get printed until he was on his deathbed.
Geocentric vs. Heliocentric
Now we know that neither of these is true. Our current understanding of the universe suggests (requires) that there is no center.
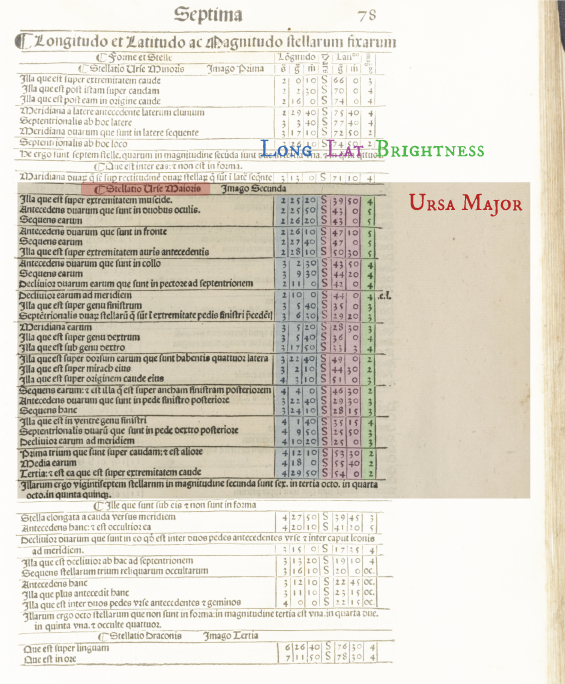
Positions of Celestial Objects
A page from Ptolemy's star catalog
The positions of the stars where recorded by constellation groups, with reference to the sun. Also included where the brightness's, ranked on a rudimentary 6 tier scale.
Ptolemy's catalog in 3d space
The Altitude-Azimuth Coordinate System
The altitude-azimuth measurement scheme. Only useful if everyone is located at the same point on the earth, which they are obviously not.
The most basic method of describing the position of a celestial body is to use the altitude-azimuth coordinate system . All that is required is two measurements: the altitude ($h$) which is defined as the angle measured from the horizon to the object along a great circle , and the azimuth , ($A$) which is the angle measured eastward along the horizon from the north pole to the great circle used for the altitude measurement. One can also use the zenith distance ($z$) to indicate the angle measured from the zenith to the object. Note that $z + h = 90^\circ$.
This method is also called the horizon coordinate system since it is based on the observer's horizon. This implies that the measurements will be different for different observers, which is a major limitation of this coordinate system.
The Equatorial Coordinate System
RA and Dec are a more universal way to describe positions in the sky. Rather than the earth serving as the reference, the locations of celestial objects becomes the reference framework.
The equatorial coordinate system is able to overcome the limitations of the altitude-azimuth system by defining positions with respect to features in the sky and is therefore not dependent on the observers position.
The two variables we will use are the declination : ($\delta$) and the right ascension ($\alpha$). To understand what these two angles are measured with respect to, we need to understand the earth's orbit in more detail.
Basics of the earth's orbit
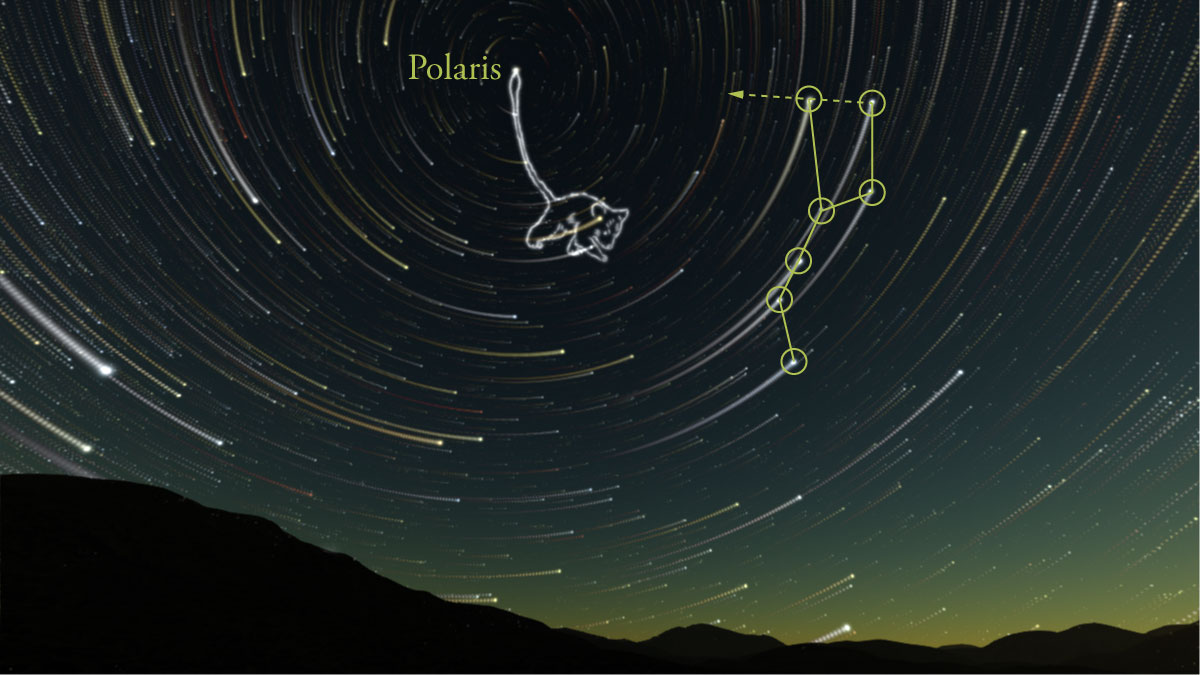
The north celestial pole is near the star called Polaris. (This changes though)
Celestial equator
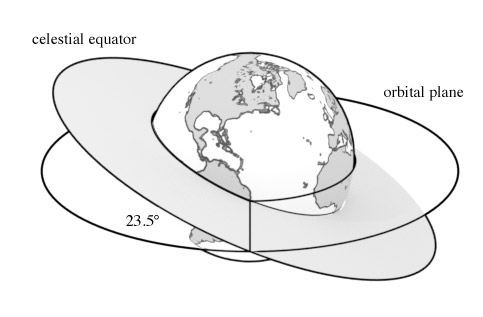
The earth is titled with respect to its orbital plane. If we imagine a plane that passes through the equator of earth, and extend it outward in all directions, this will be the celestial plane.
Equatorial System
Here is some output from JPL Horizons database:
*******************************************************************************
Date__(UT)__HR:MN R.A.__(a-apparent)__DEC Azi____(a-app)___Elev
*********************************************************************
$$SOE
2023-Jan-30 17:00 *m 20 51 55.49 -17 35 56.9 177.420437 31.609851
2023-Jan-31 17:00 * 20 56 01.16 -17 19 16.2 177.366060 31.886346
$$EOE
*******************************************************************************
Tool is here: https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons/app.html#/
Units
Deg Min Sec
Hours Min Sec
Decimal
Special Times of the year
The Ecliptic
The position of the sun in the sky varies throughout the year. The position of the sun at the time of the vernal equinox is one of our main reference points for determining the position of the object. We'll say that that location has a right ascension of 0. A declination of 0 will be given by position aligned with the celestial equator.
Analemma
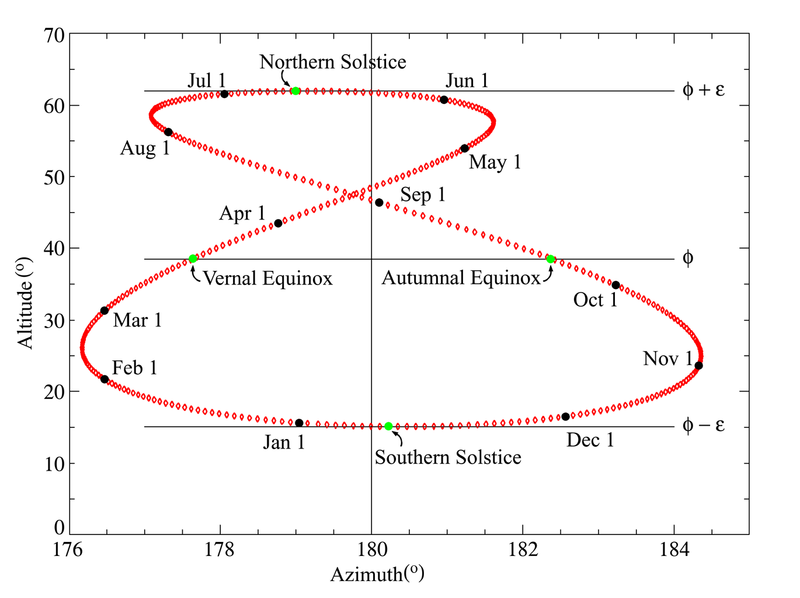
An Analemma Plot:
The plot here shows the position of the sun at 12pm over the course of one full year. The day when the sun is the highest in the sky is called the summer solstice . When it is at the lowest point is called the winter solstice . The two days right in the middle of the solstices are called the equinox: autumnal and vernal. (or fall and spring)
What is the lowest latitude from which all the stars of the big dipper are visible? Below which latitude is the big dipper never visible at all?
Time
Time keeping and astronomy are linked. The day is defined by the change in position of the sun.
Warren Field, Aberdeenshire Scotland, 8th Millennium BC. Used to track lunar
Solar vs. Sidereal Time
Solar and Sidereal time compared. The earth has to rotate about 1 degree more for the sun reach the same point in the sky, than the rotation needed for the fixed stars to return to the same point.
If the Earth rotates around its own axis exactly once, the distant stars will appear to be in the same position. However, the sun will not! The earth needs to rotate about 1 degree more in order for the sun to be in the same place in the sky. Thus we have two 'days'. The solar day is the time it takes for the sun to cross the merdian again (24 hours) while the sidereal day is the time it takes to rotate exactly once. (It's about 4 minutes less).
Let's call the angular velocity of the Earth in it's orbit, with reference to the stars: $\overrightarrow{\omega}_E$. The rotation of the Earth around it's own axis (relative to the stars) will be $\overrightarrow{\omega}_\textrm{sid}$. If we asked the sun how quickly the earth was rotating (i.e. in the solar reference frame) we would find that the $\overrightarrow{\omega}_\textrm{sol}$ would be equal to the difference between $\overrightarrow{\omega}_\textrm{sid}$ and $\overrightarrow{\omega}_E$, which leads to the following:
$$\begin{equation}
\overrightarrow{\omega}_\textrm{sid} = \overrightarrow{\omega}_\textrm{sol} + \overrightarrow{\omega}_E
\end{equation}$$
Since the vectors are approximately parallel (the're not, but we can ignore the 23.5°), the we can write a scalar equation:
$$\begin{equation}
\omega_\textrm{sid} = \omega_\textrm{sol} + \omega_\textrm{E}
\end{equation}$$
Since $\omega = \frac{2\pi}{P}$ ($P$ is the period) we can write:
$$\begin{equation}
\frac{1}{P_\textrm{sid}} = \frac{1}{P_\textrm{sol}} + \frac{1}{P_E}
\end{equation}$$
Our definition of the solar period is 1 day, then $P_E \approx 365$ days which is much greater than $P_\textrm{sol}$ and we can make the following approximation:
$$\begin{equation}
P_\textrm{sid} = \left(\frac{1}{P_\textrm{sol}}+\frac{1}{P_E} \right)^{-1} = P_\textrm{sol} \left( 1+ \frac{P_\textrm{sol}}{P_E}\right)^{-1} \approx P_\textrm{sol}\left( 1 - \frac{P_\textrm{sol}}{P_E} \right)
\end{equation}$$
Solving for the difference the $P_\textrm{sol}$ and $P_\textrm{sid}$:
$$\begin{equation}
P_\textrm{sol} - P_\textrm{sid} = \frac{(P_\textrm{sol})^2}{P_E} = \frac{1}{365}
\end{equation}$$
which when converted to minutes give about 3.95 minutes difference between a solar day and a sidereal day.
Julian Date
You can't do math with date formats, so we need to have a different system. We set the 0 day to be January 1 4713 BC, at noon. Every day after that just adds 1. January 1st of 2017 will have been 2457755 days since then so we can say the JD is 2457755 (at noon). Times other noon just get fractional descriptions. The Modified Julian Date is very similar, except that it starts at midnight, so noon on January 1st would be 2457755.5 MJD.
Easter over a few thousand years
https://statisticsbyjim.com/fun/when-is-easter-this-year/
Summary
Ptolemaic vs. Copernican
Position of Celestial Objects
Basics of Earth's orbit
Solar vs. Sidereal
Modern Timekeeping
Bibliography and Further Reading
Kuhn, T The Copernican Revolution (Harvard University Press, 1957)
Sobel, D. A More Perfect Heaven (New York: Bloomsbury Publishing USA, 2001)
Copernicus - De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
Ptolemy - The Almagest