Instruments
Basic Optics
Rays of Light
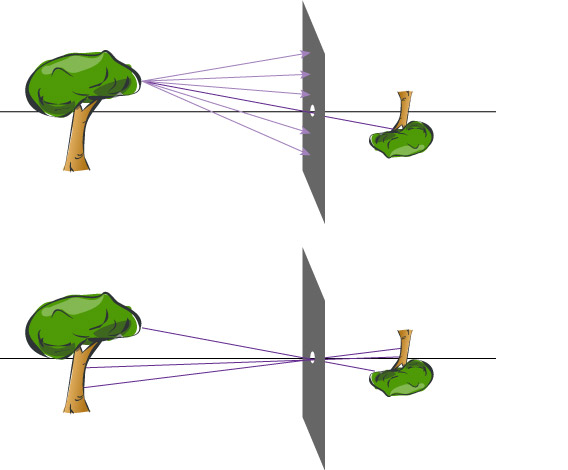
A pinhole will project an inverted image on a plane.
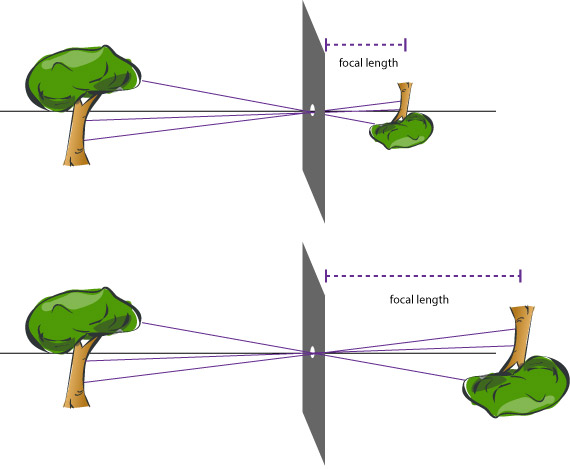
The image will be in focus everywhere. It's size changes based on the position of the focal plane.
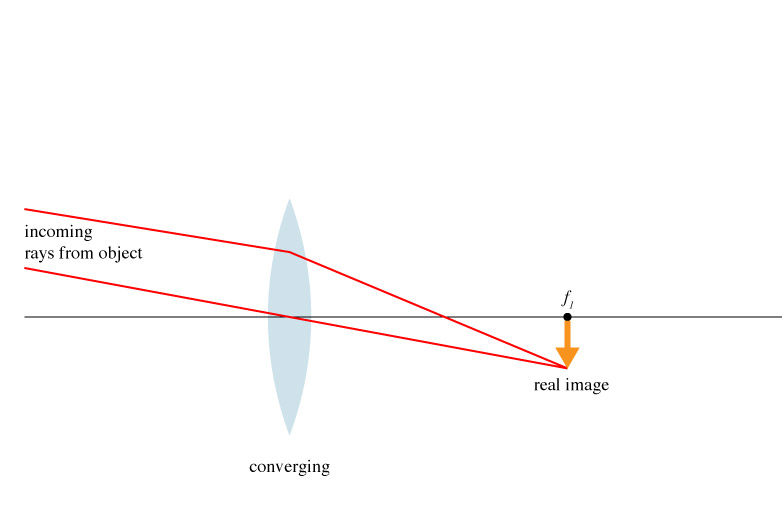
Converging Lens
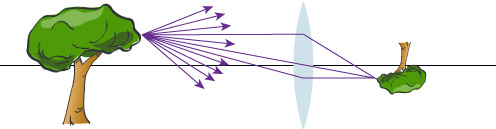
Images
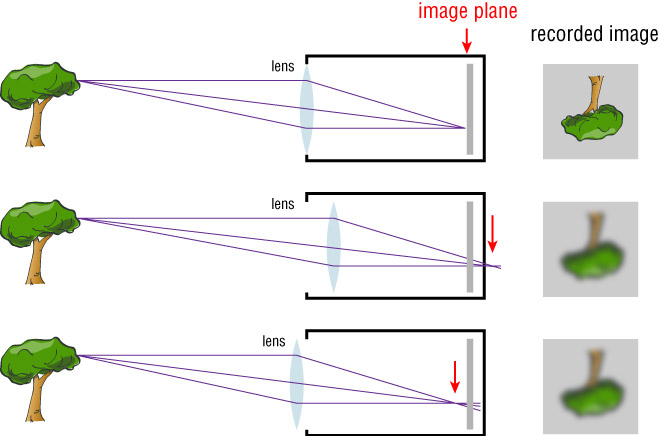
Changing the position of the screen will result in a blurry image.
Light from stars
Two stars separated by an angle $\theta$ in the sky, will create images separated by a distance $d$ on the detection screen.
Waves of light
Airy Disc
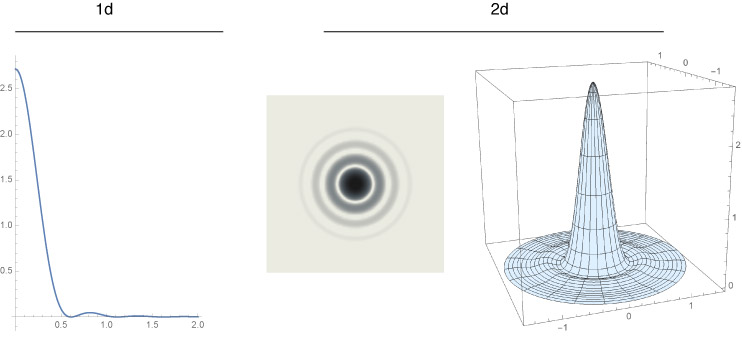
There is a limit
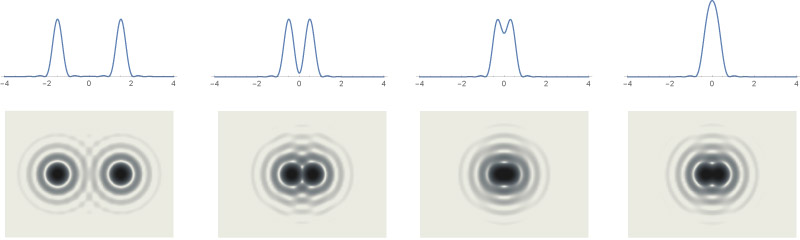
Two point sources getting closer.
Unresolved point sources
Rayleigh Criterion
$$\theta_{\textrm{min}} = 1.22 \frac{\lambda}{D}$$
Basic Imaging Systems
The eye
The human eye
focusing the eye
Focusing the eye
A Basic Telescope
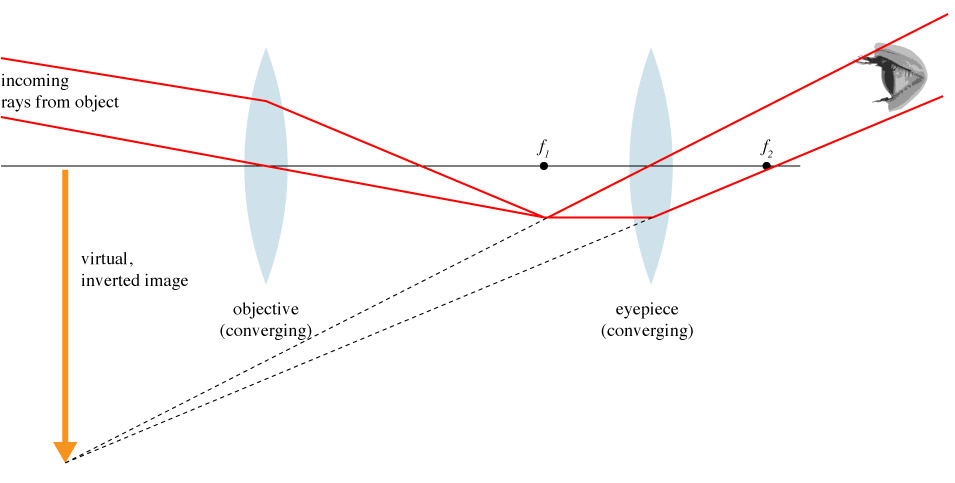
Magnification: $$\begin{equation} M = \frac{f_1}{f_2} = \frac{f_{\textrm{objective}}}{f_\textrm{eyepiece}} \end{equation}$$
Aberrations
Lenses aren't perfect.
Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic Aberrations
Different Colors with have different focal points
Spherical Aberration
Spherical Aberrations
Fixing aberrations
Fixing Aberrations
Mirrors
A mirror ray diagram
Some Real Instruments
Galileo's Telescope
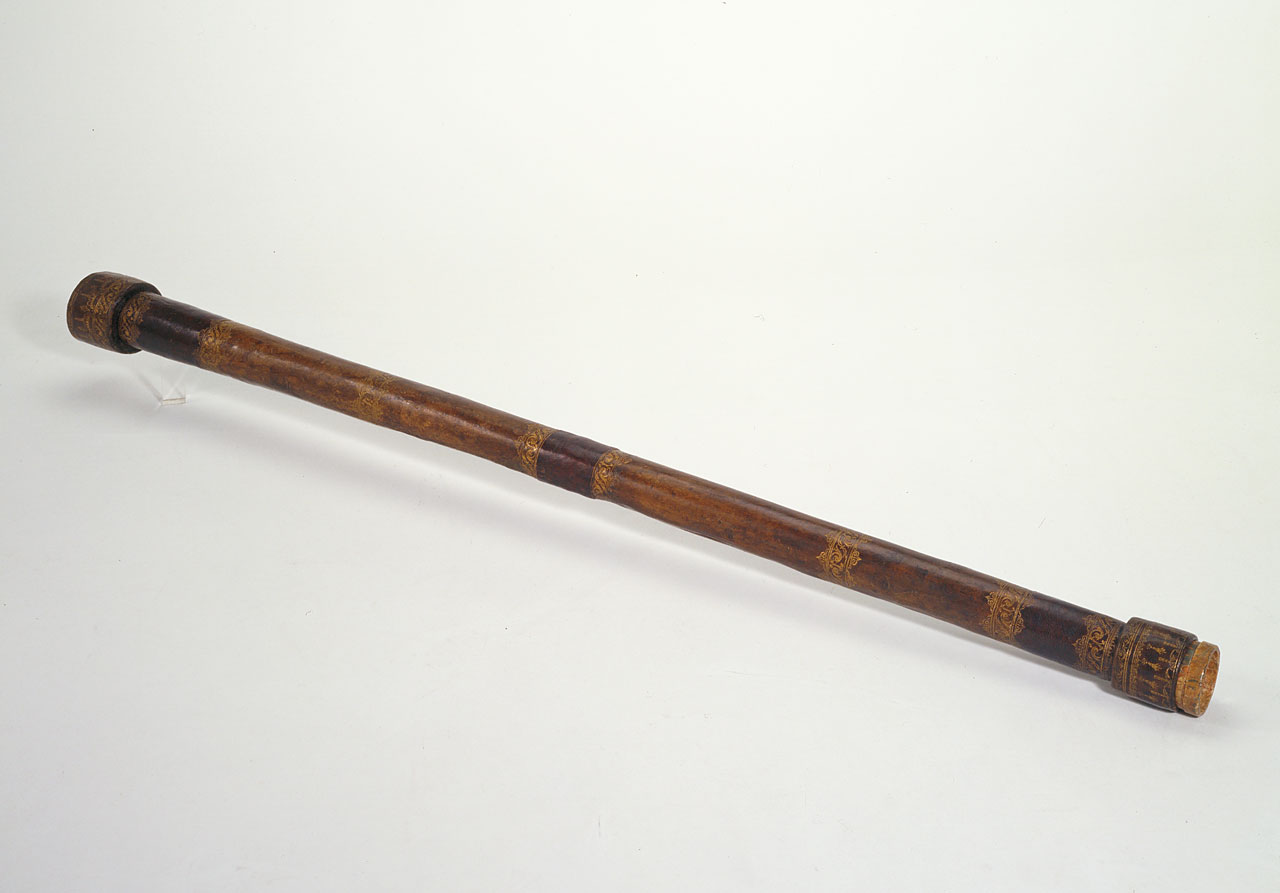

Galileo's Telescope

Saturn as viewed through Galileo's telescope
https://www.astromatic.net/2009/05/23/see-saturn-as-galileo-did
Galileo's Telescope
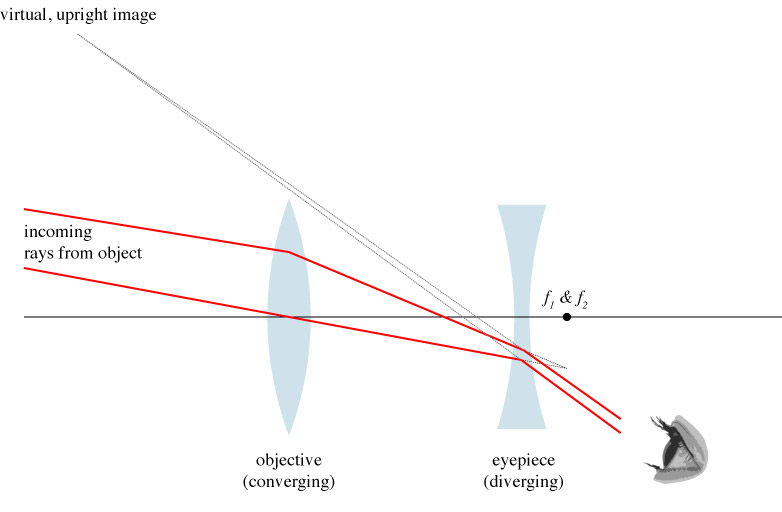
Keplerian Optics
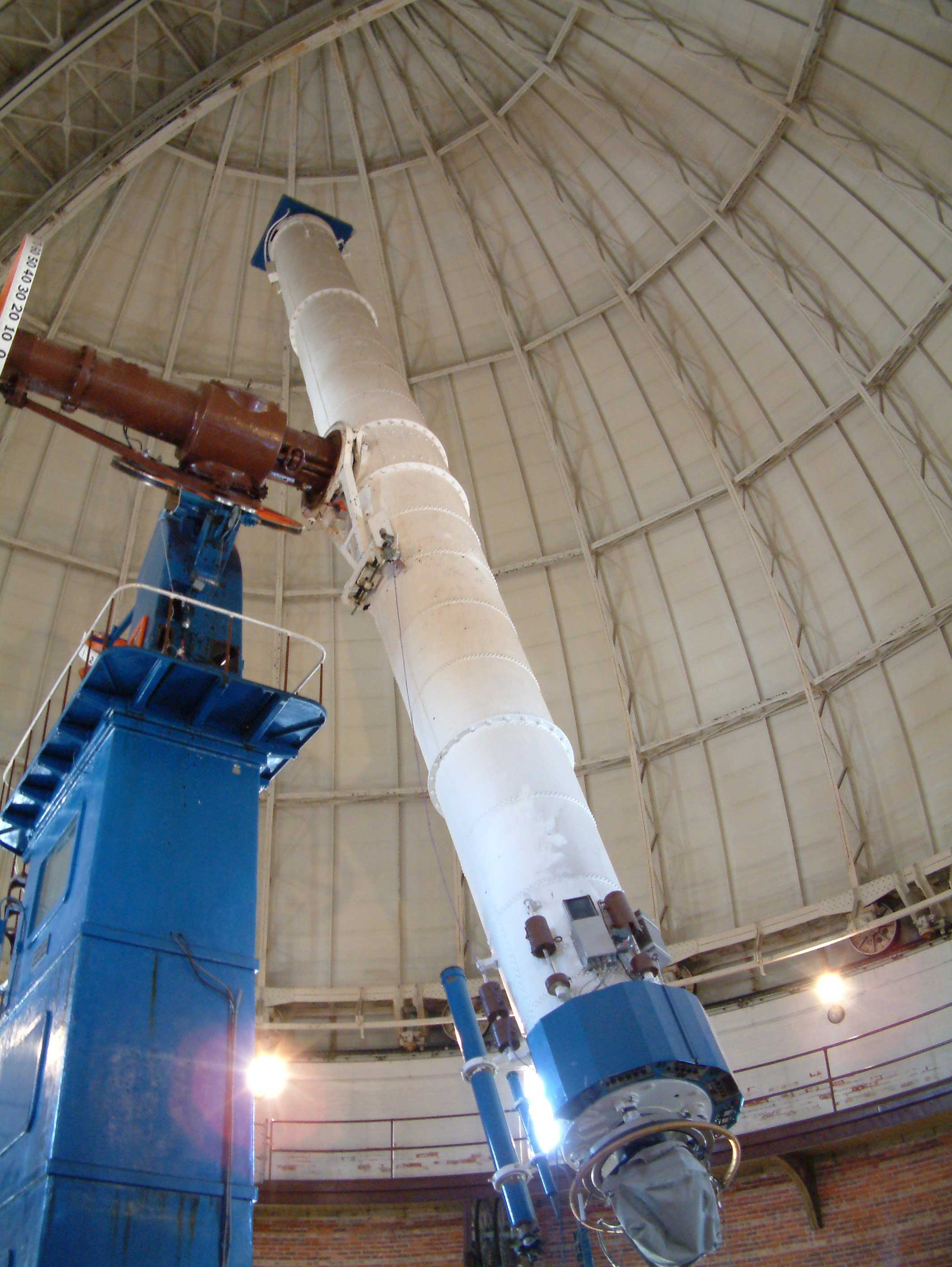

Yerkes Observatory 40 inch Refractor Telescope ( It is the largest refracting telescope used for astronomical research.) Williams Bay, Wisconsin, US
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Yerkes_40_inch_Refractor_Telescope-2006.jpg
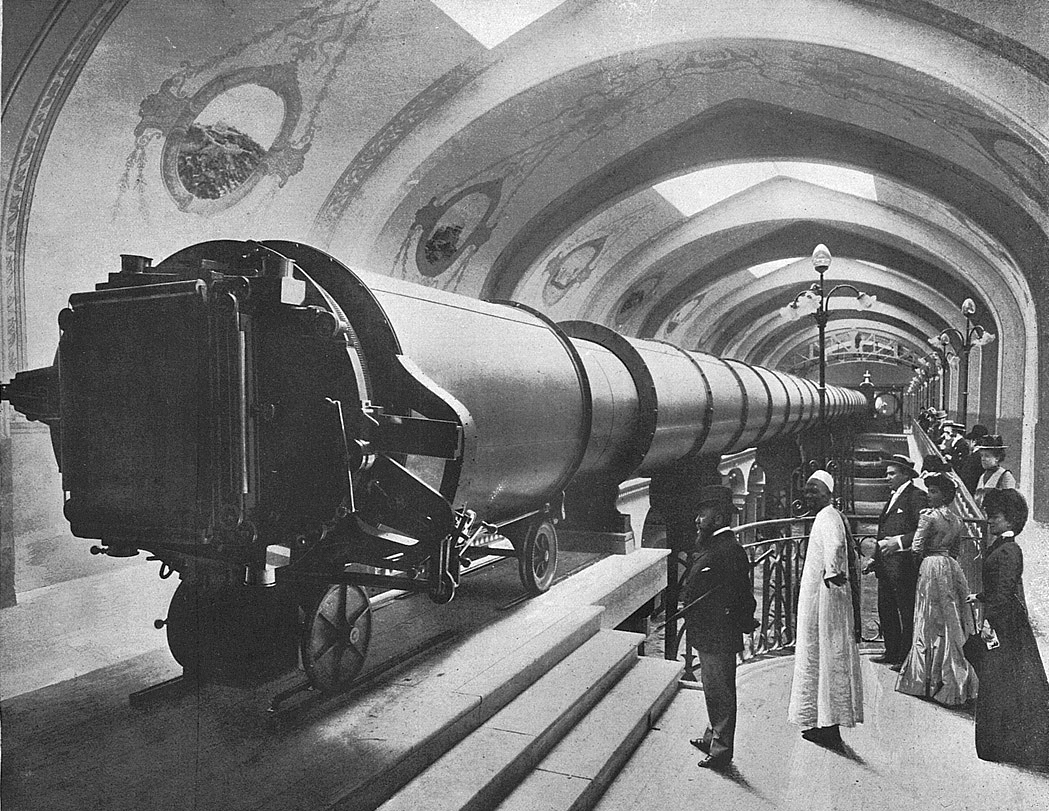

The Great Paris Exhibition Telescope of 1900, with an objective lens of 1.25 m (49 in) in diameter, was the largest refracting telescope ever constructed. It was built as the centerpiece of the Paris Universal Exhibition of 1900. 200 ft long. Too big to use.
By Unknown - Le panorama (Paris, 1900)., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=20083299
A reflecting Telescope
A reflecting Telescope
Newton's Telescope
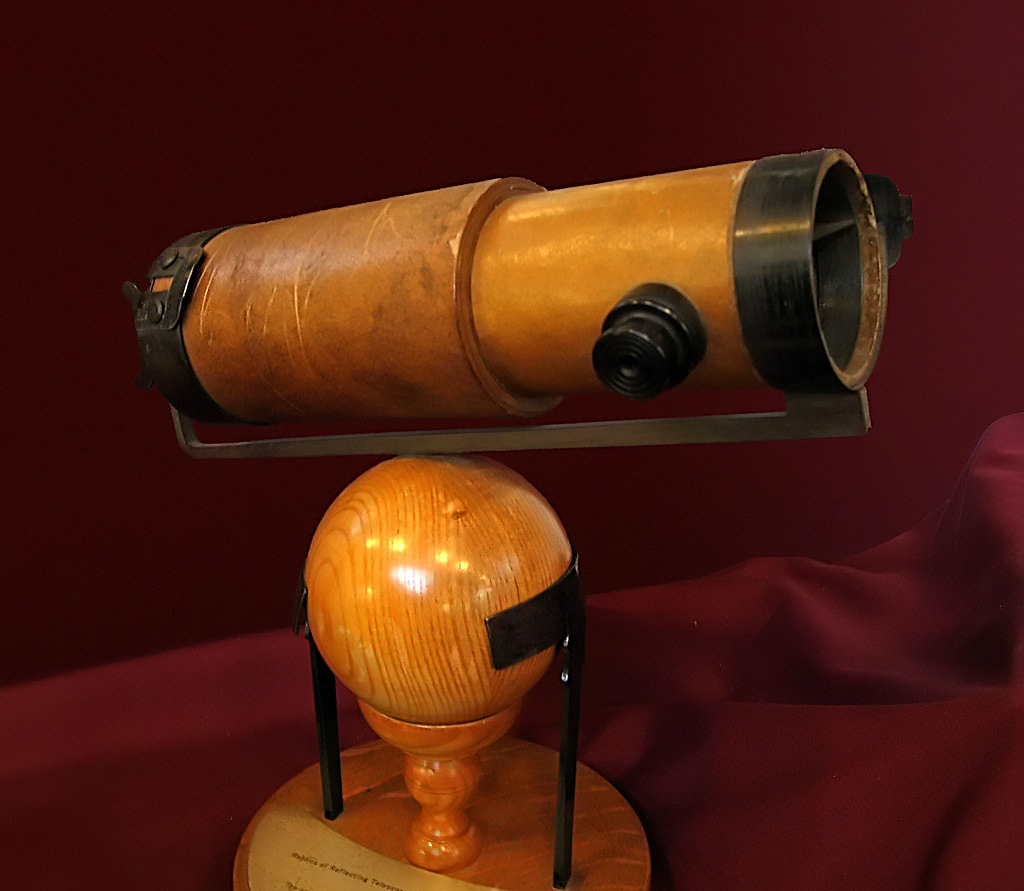

A replica of the Newton - Wickins telescope, Newton's third reflecting telescope that was presented to the Royal Society in 1766 after being restored by Thomas Heath. It is described as the better of the instruments Newton built
By User:Solipsist (Andrew Dunn) - www.andrewdunnphoto.com, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=513483
Where should we put these telescopes?
Astronomical seeing
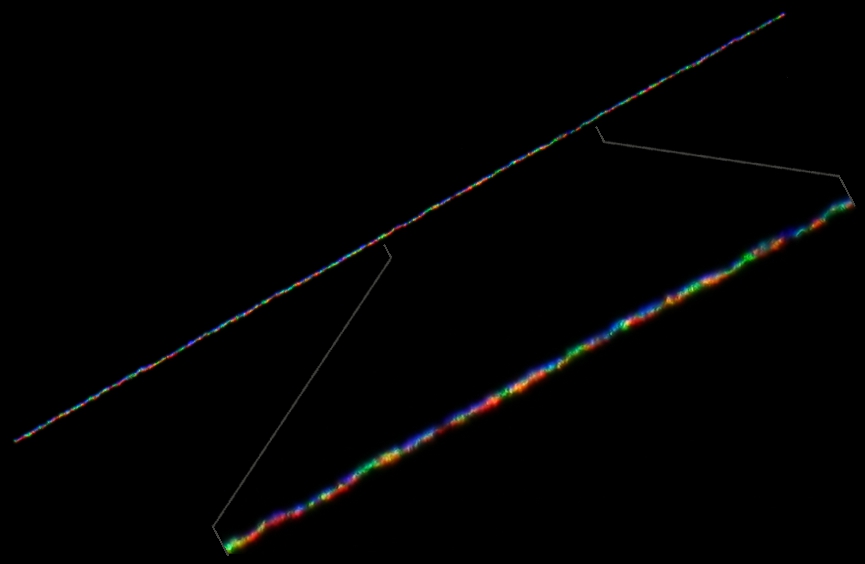
Scintillation of a star, over time
http://spaceweathergallery.com/indiv_upload.php?upload_id=124490

Moon Seeing Effect

Mountain in the atmosphere
Detectors
Charge-coupled Device: CCD
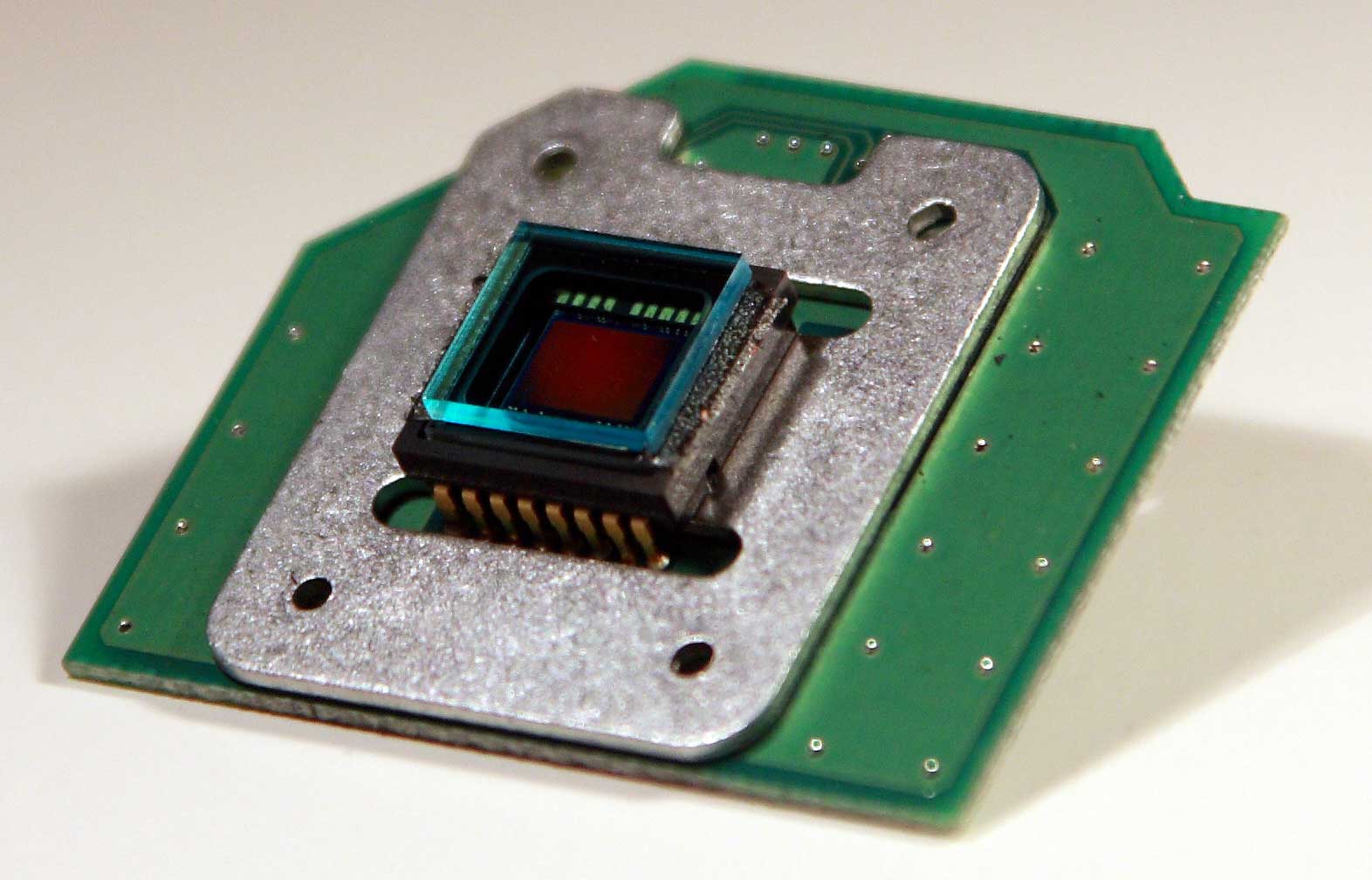
A CCD device
Other Wavelengths
The transparency of the atmosphere
Adapted from https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/RemoteSensing/remote_04.php
Radio Telescopes
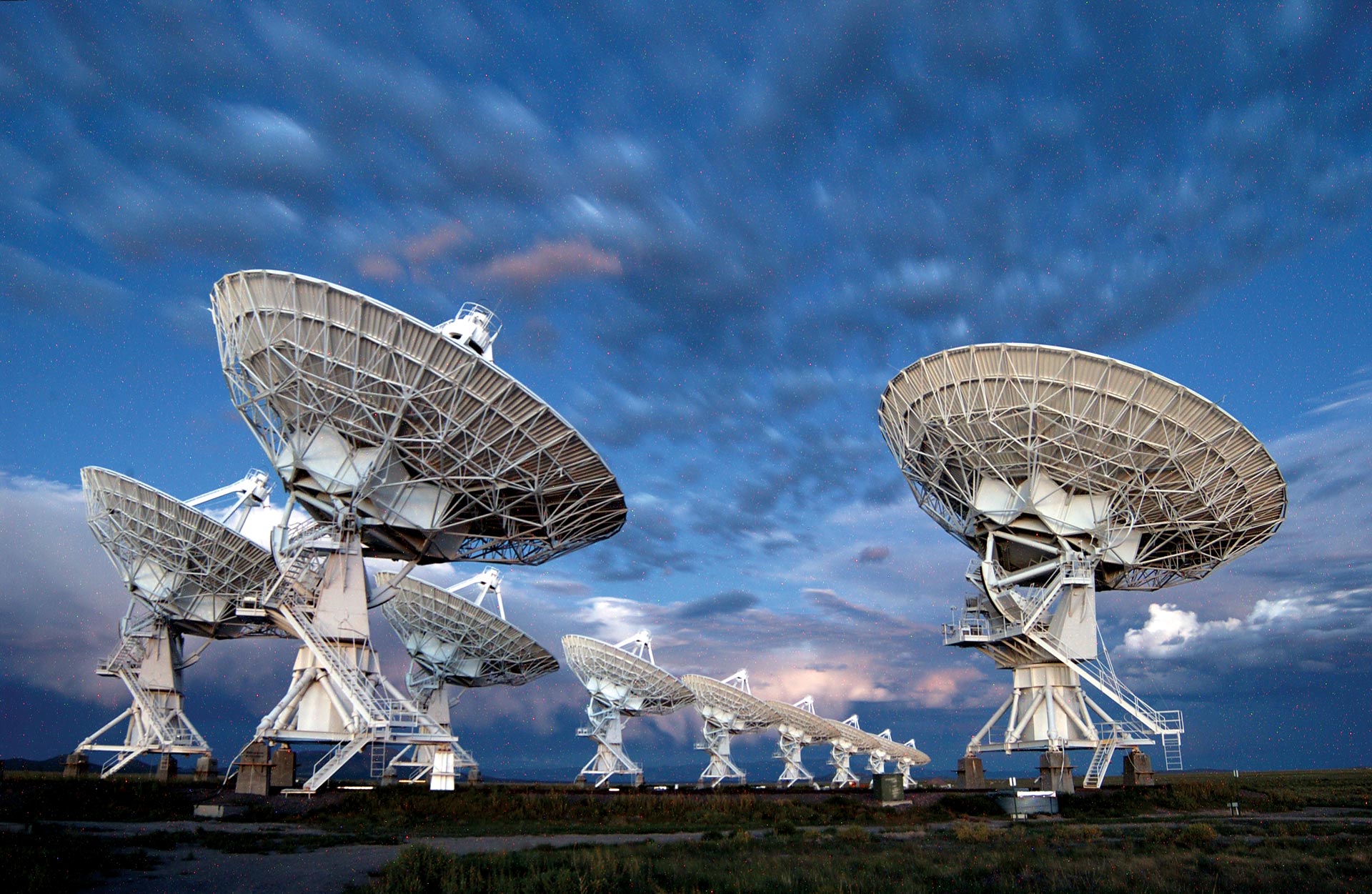

Clouds linger at twilight over the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array in its most compact configuration.
Credit: NRAO/AUI/NSF link
What if $\lambda$ is really big? $$\theta_{\textrm{min}} = 1.22 \frac{\lambda}{D}$$
Arecibo
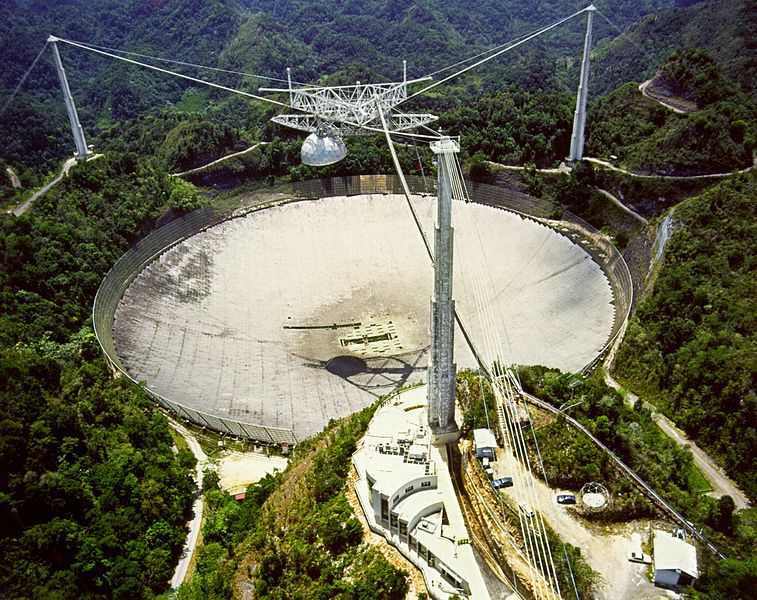

Credit: Author H. Schweiker/WIYN and NOAO/AURA/NSF link
Orbiting Astronomical Observatory
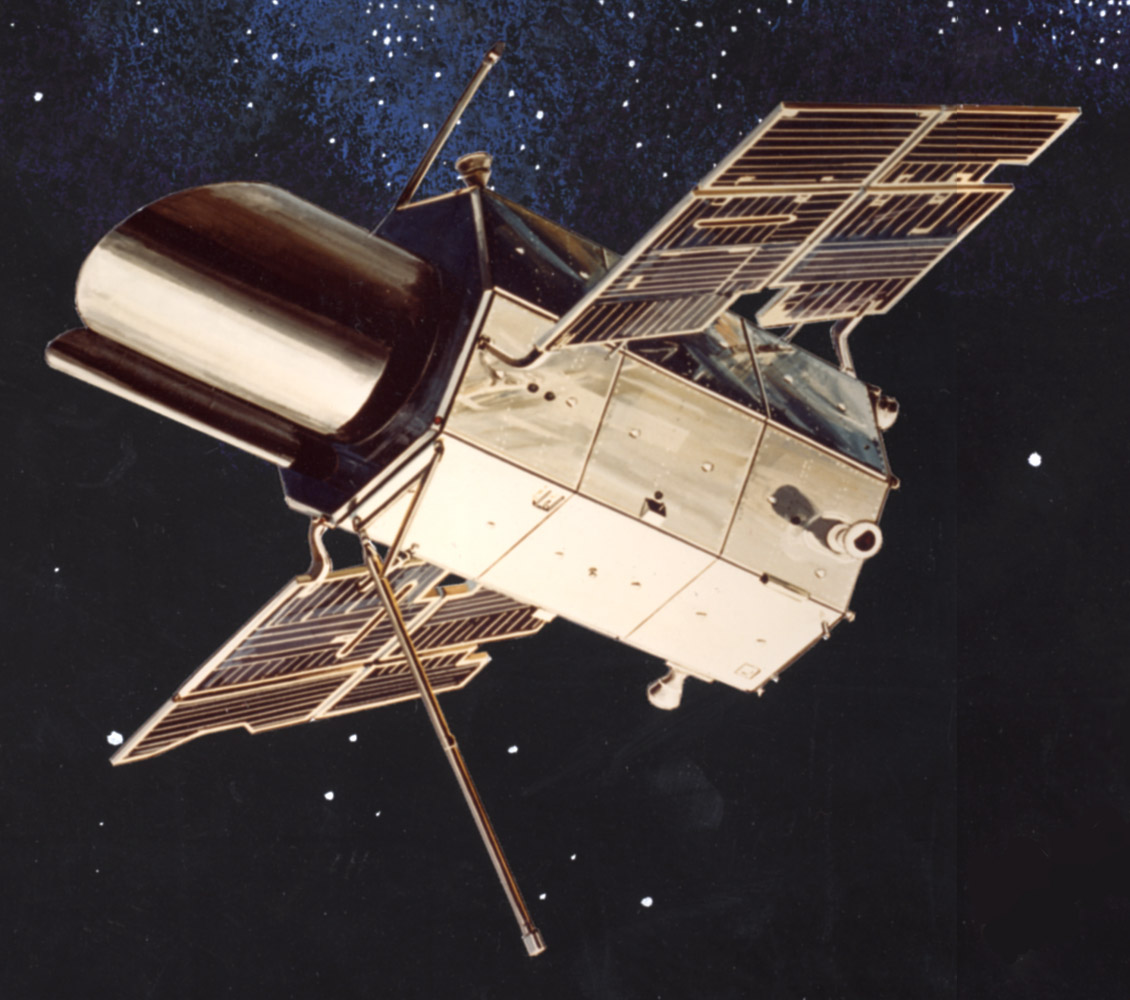

The Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (OAO) satellites were a series of four American space observatories launched by NASA between 1966 and 1972, which provided the first high-quality observations of many objects in ultraviolet light.
Let's put a telescope above the atmosphere. There, instruments will be able to reach the diffraction limit mentioned above, rather than the seeing limit of ground based observatories.
Hubble
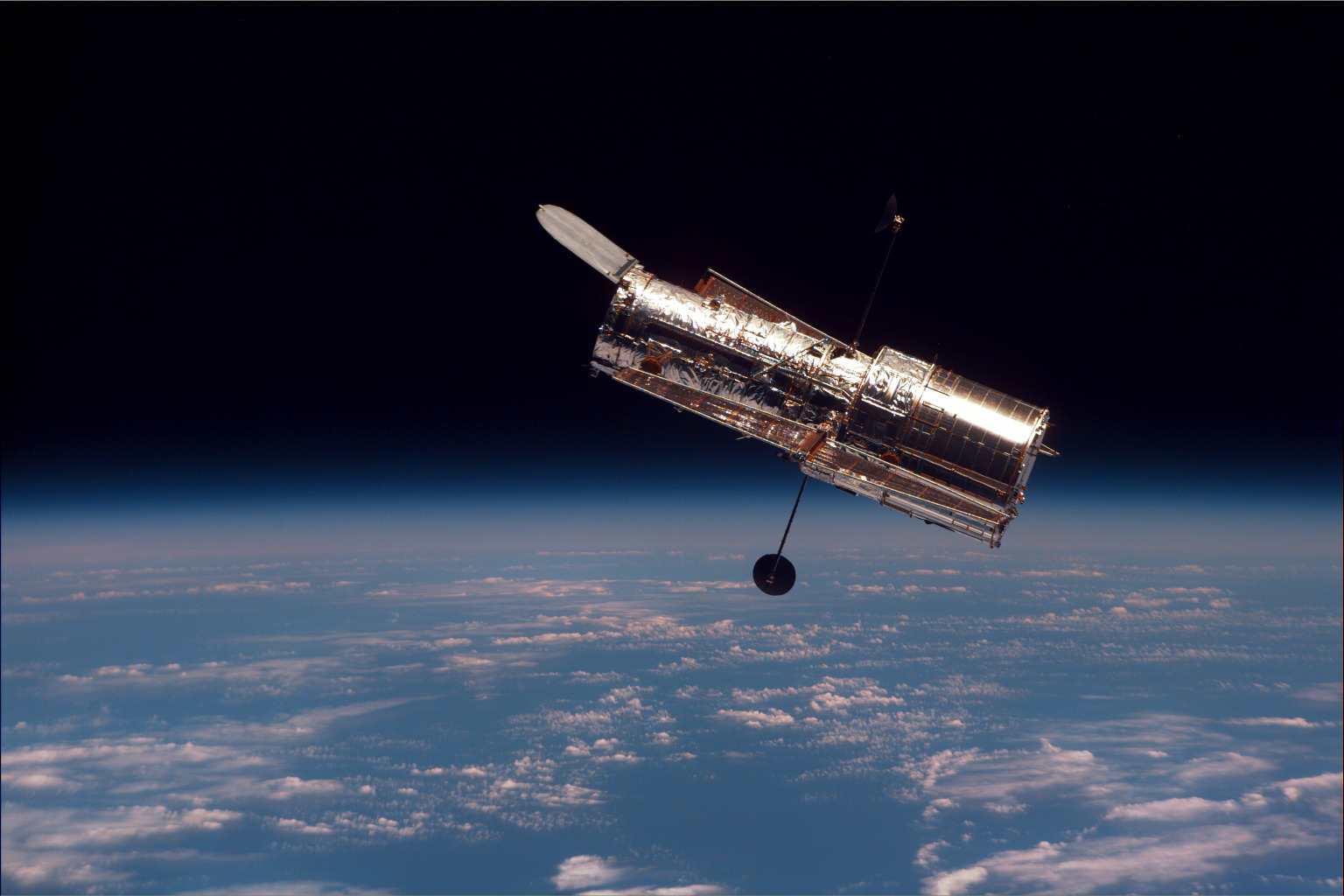

The Hubble Space Telescope
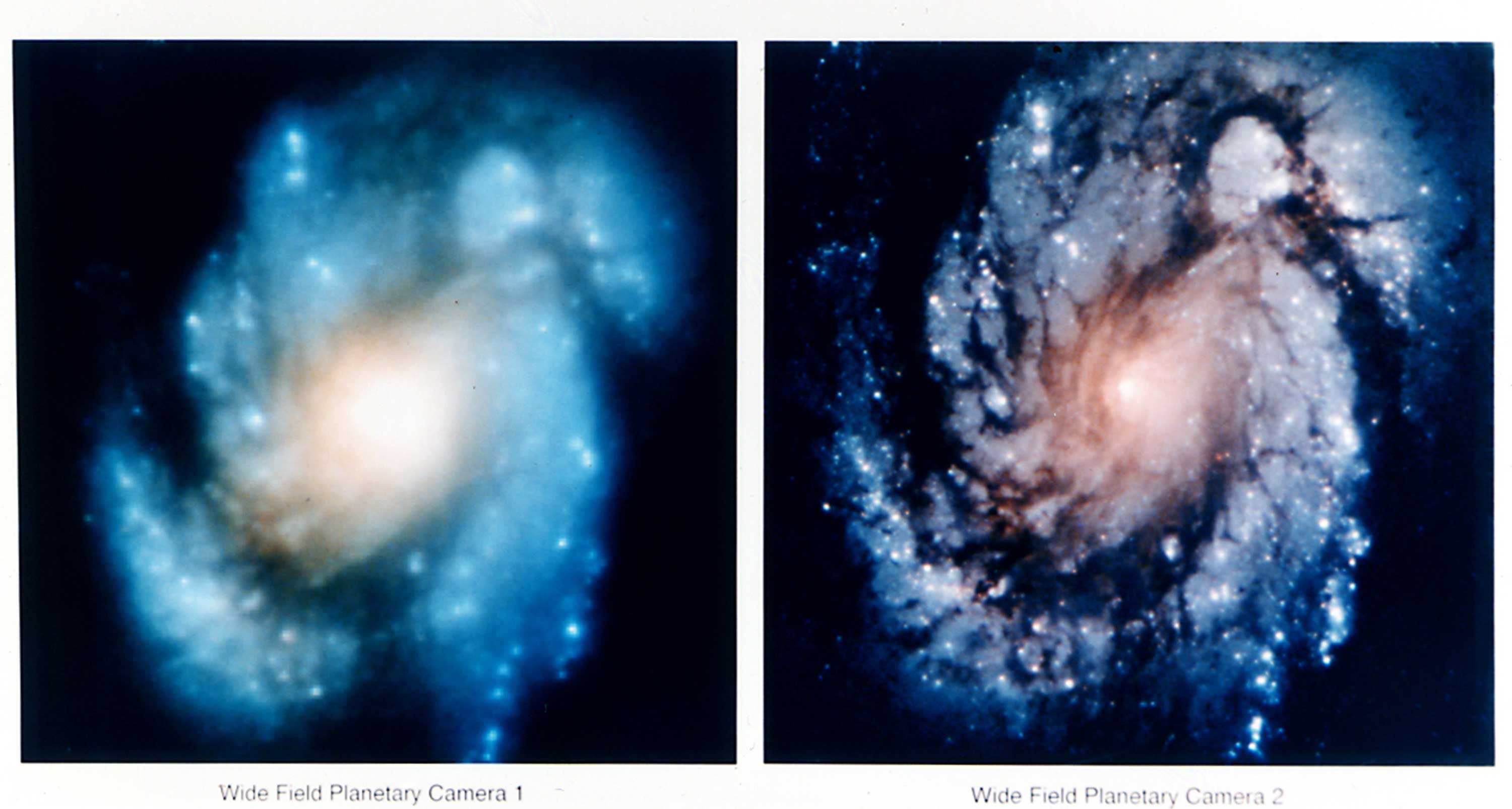

Hubble before and after
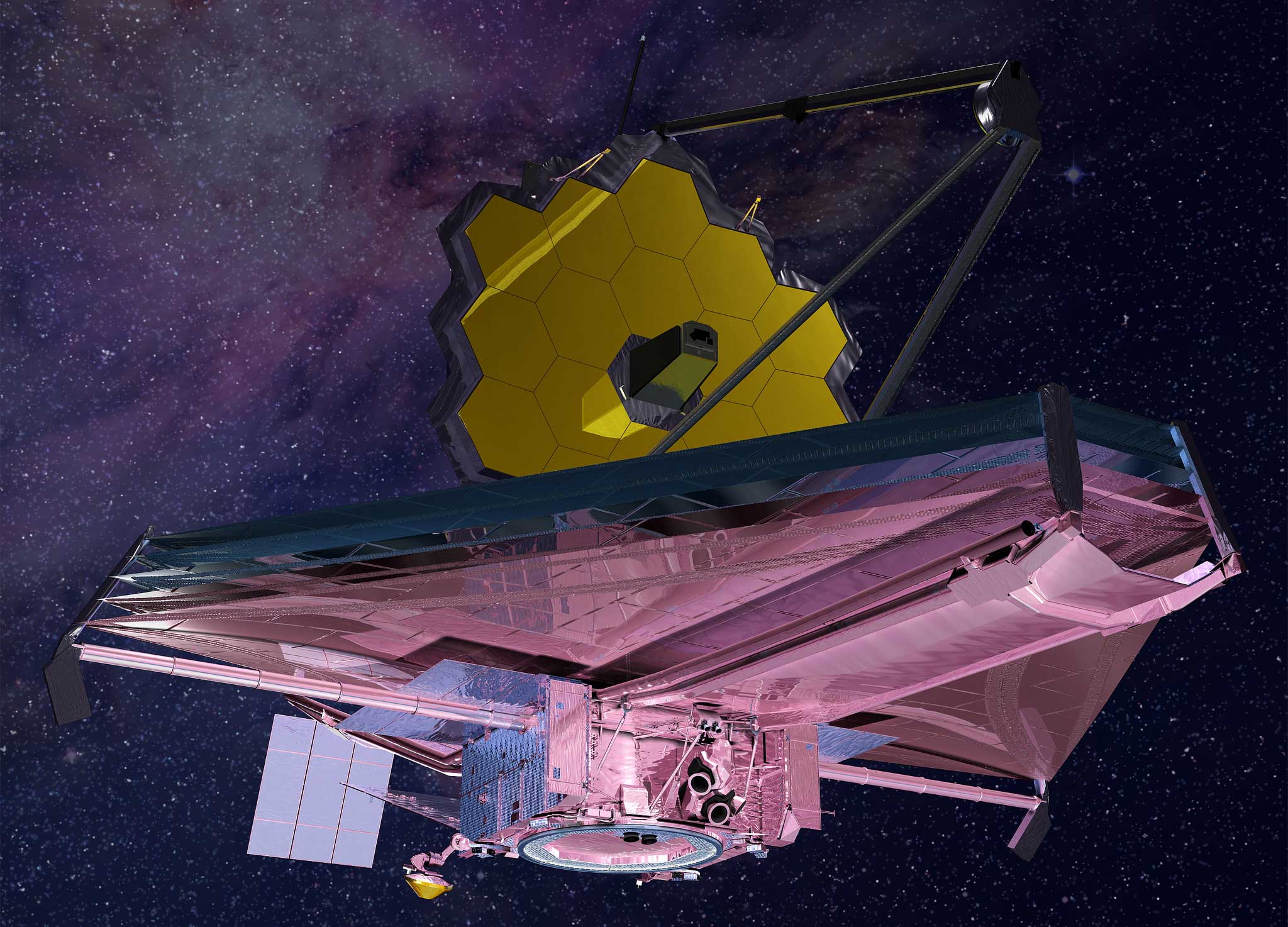

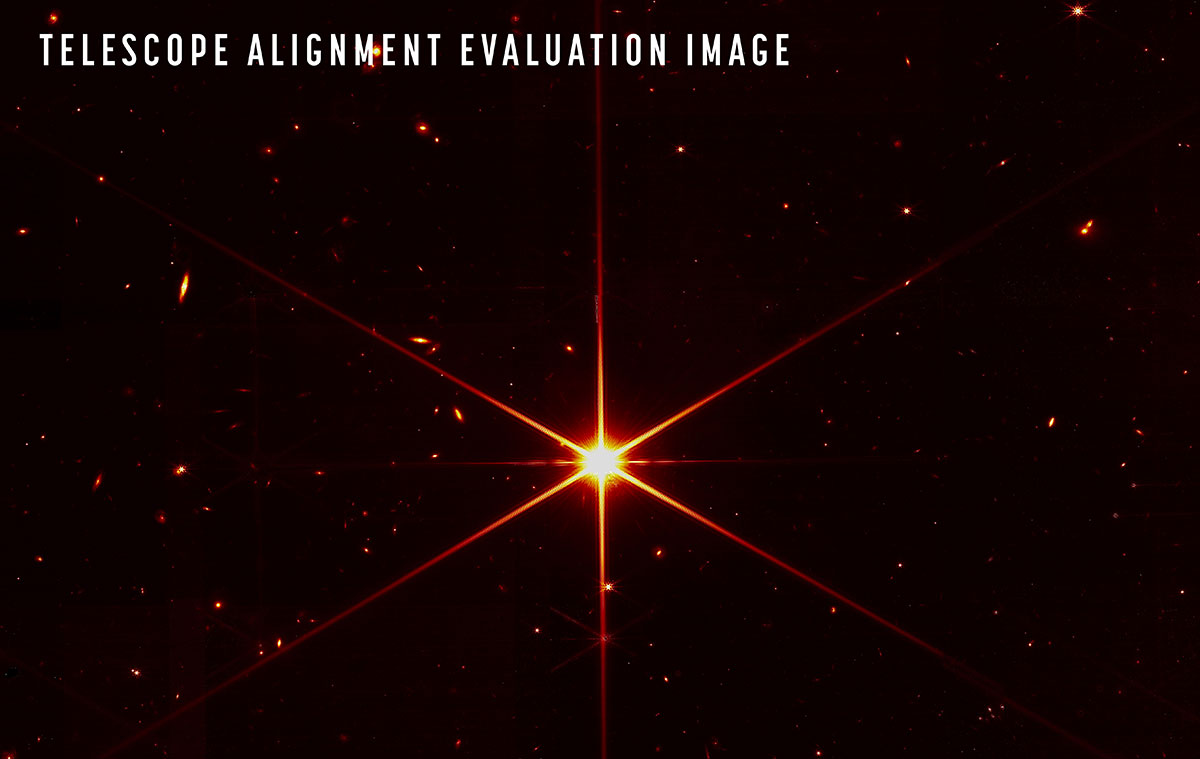
The telescope that ate astronomy.
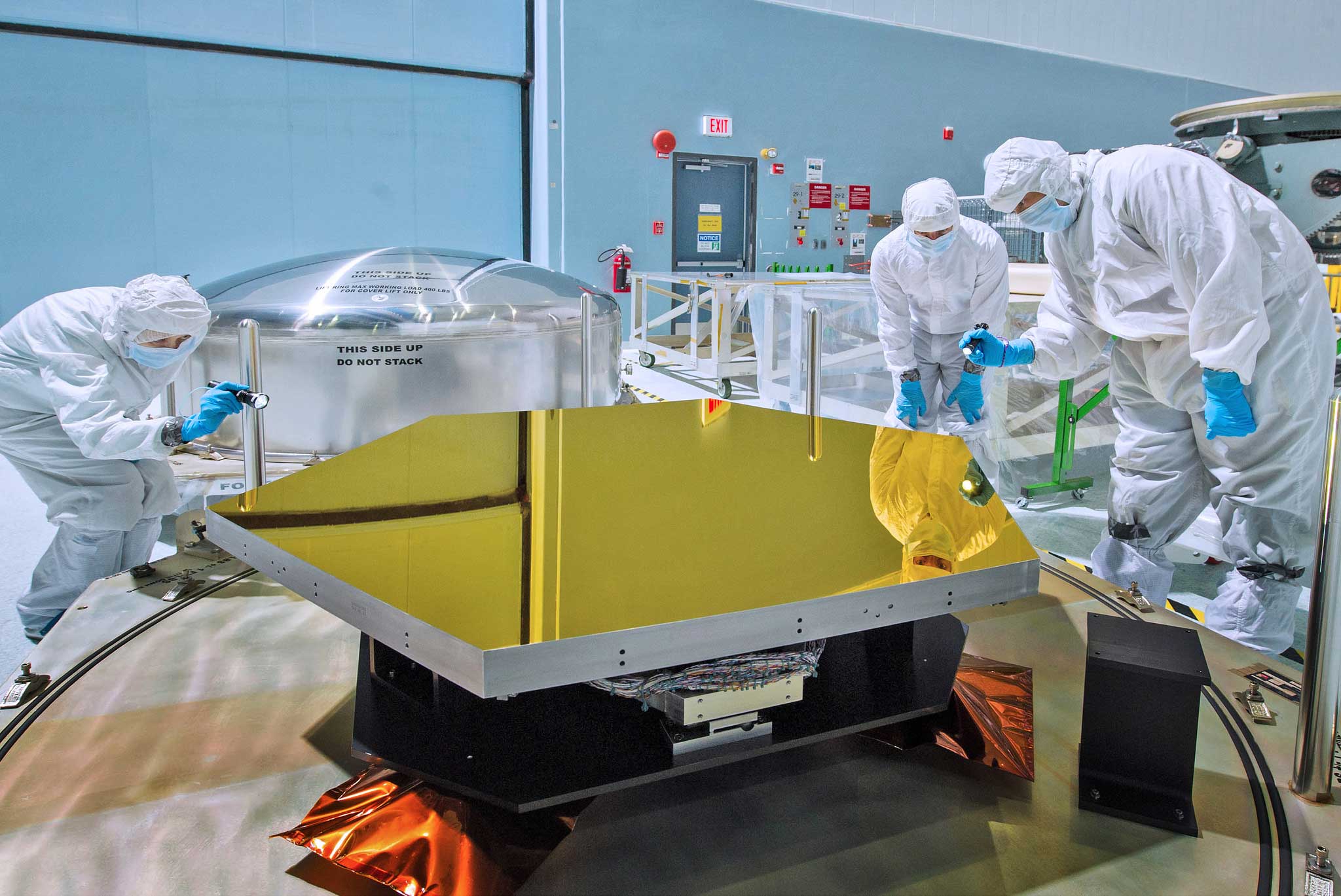

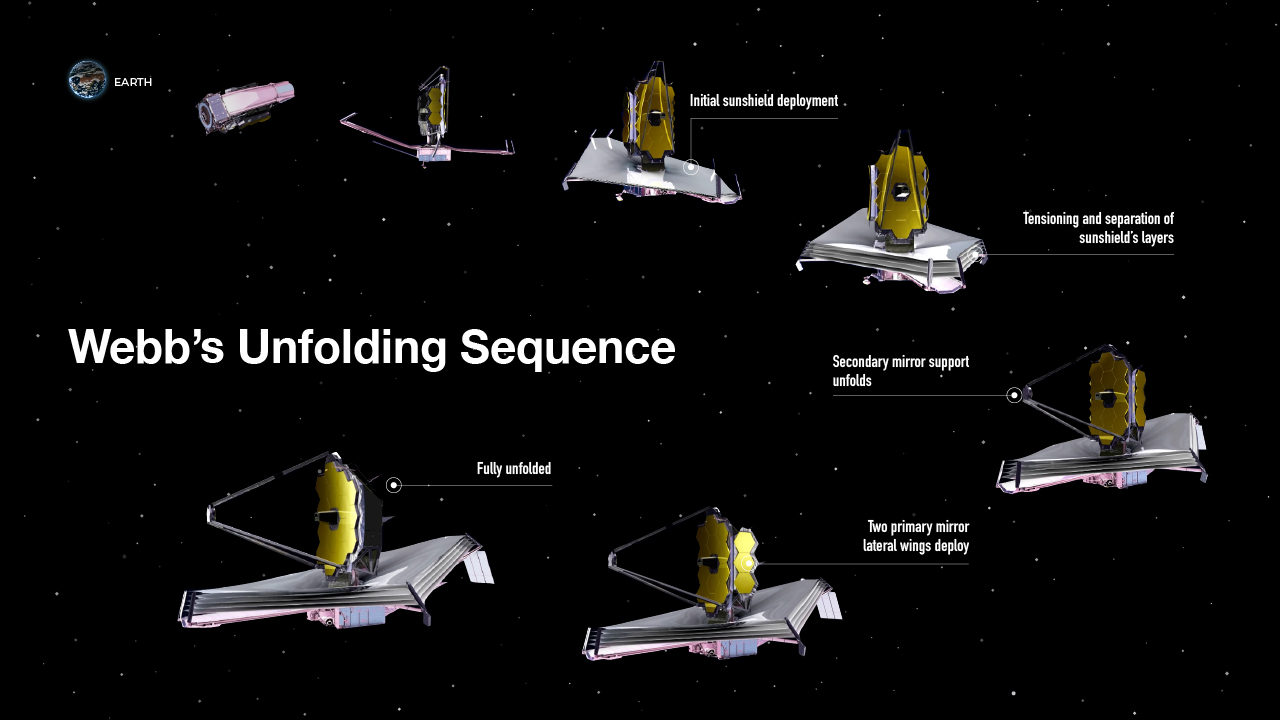
Inspecting the mirrors on the James Webb Space Telescope
Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn - https://www.flickr.com/photos/nasawebbtelescope/8047310260
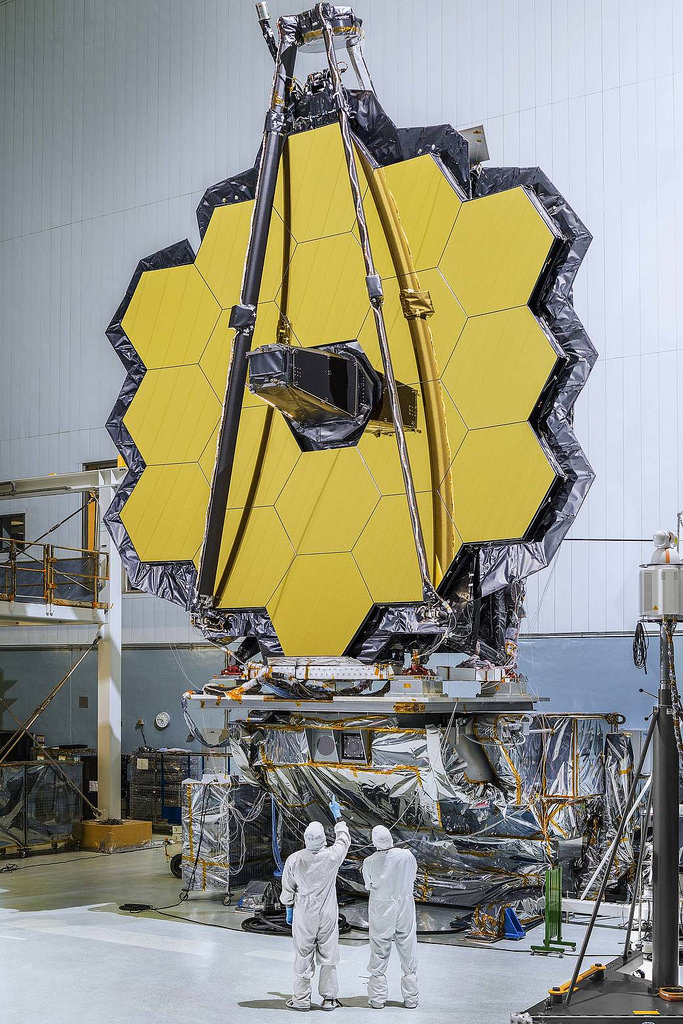

The primary mirror of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, consisting of 18 hexagonal mirrors, looks like a giant puzzle piece standing in the massive clean room of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Image Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn - https://www.flickr.com/photos/nasawebbtelescope/30116152713/
Other improvements
- Active Optics - mirrors that move.
- Adaptive Optics - guide stars
Adaptive Optics
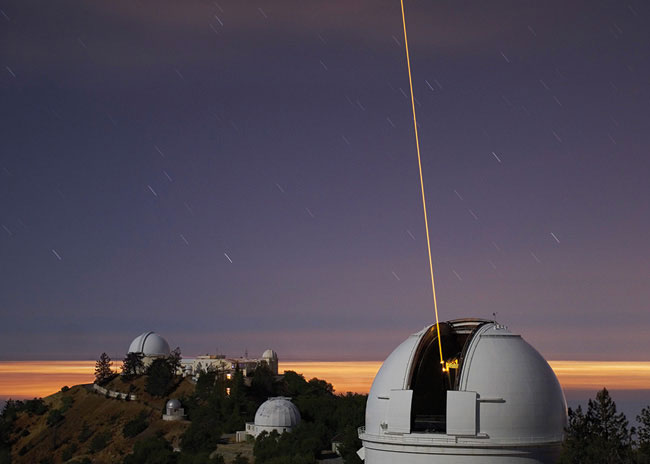

An artificial star
Make a star using a laser.

Saturn without and with Adaptive Optics
Credit: Heidi B. Hammel and Imke De Pater/WMKO Keck