Galaxies
Early Attempts to catalog and classify
Messier Catalog
A catalog of 110 astronomical objects - started in 1771
HST collection of images from the catalog
"The Great Debate"
26 April 1920
Smithsonian Museum of Natural History
Harlow Shapley's Position
All the distant nebula we could see where just small things located in the milky way. Essentially, the Milky way was the extent of the known universe.
Heber Curtis' Position
All the distant nebular were in fact other galaxies, like the milky way. "Island Universes" as Kant called them.
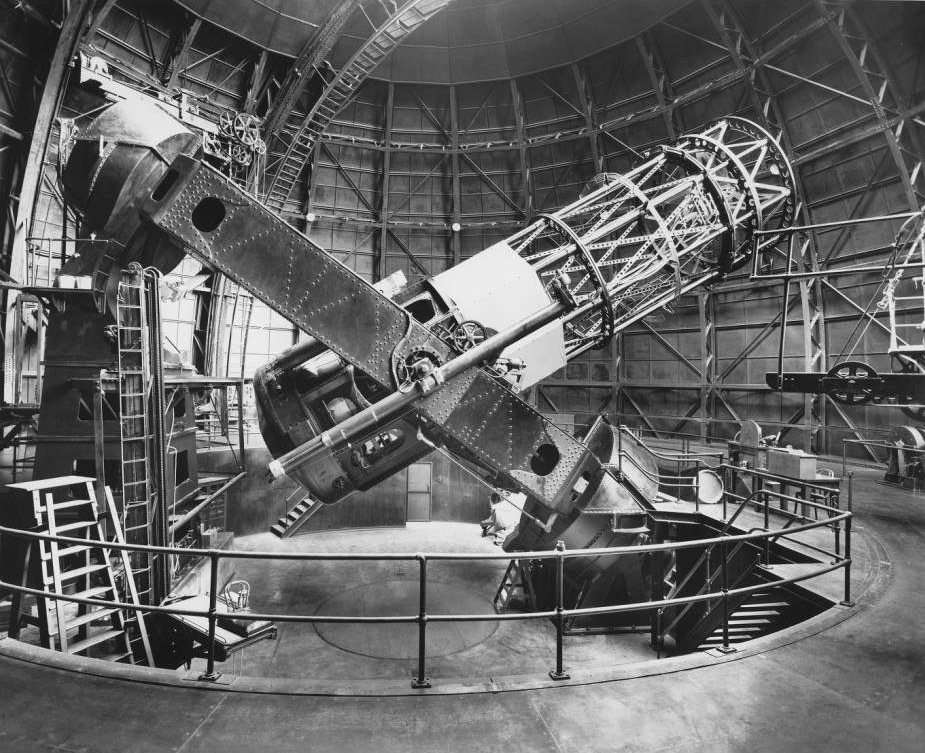

The 100 inch reflecting telescope at Mt. Wilson, near LA.
Courtesy of The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Collection at the Huntington Library, San Marino, Calif.
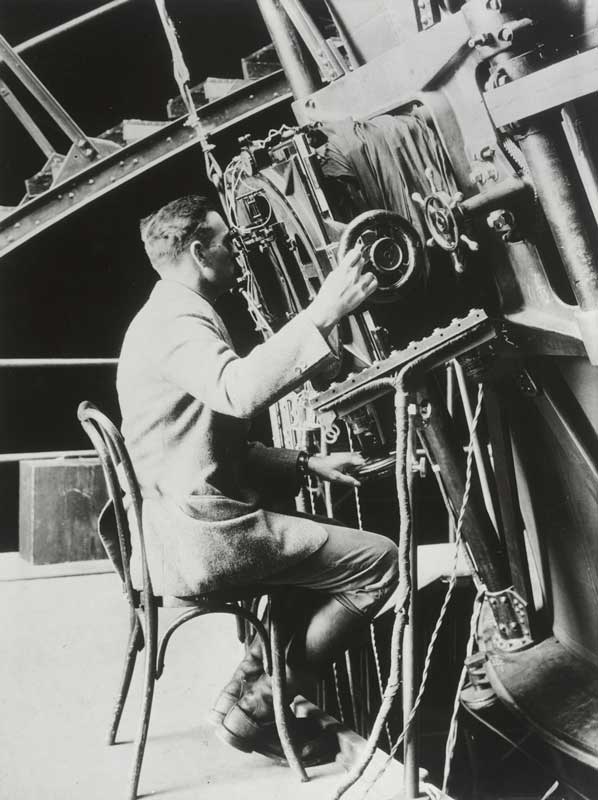

Hubble at the telescope
Edwin Hubble Papers/Courtesy of Huntington Library, San Marino, Calif.
Hubble - Andromeda
nasa
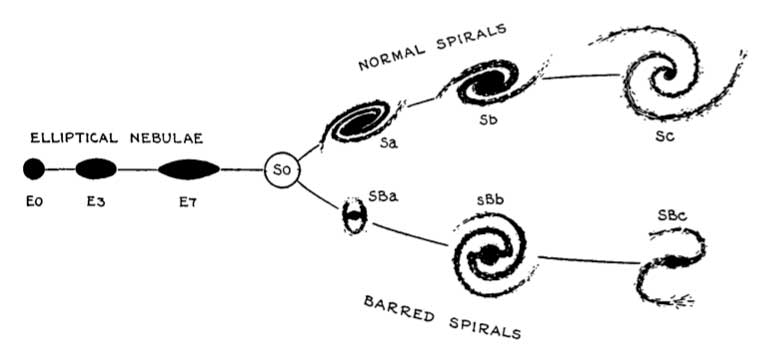
The Sequence of Nebula Types
Edwin Hubble The Realm of the Nebulae Dover Publications Inc. 1958
Spiral: Andromeda
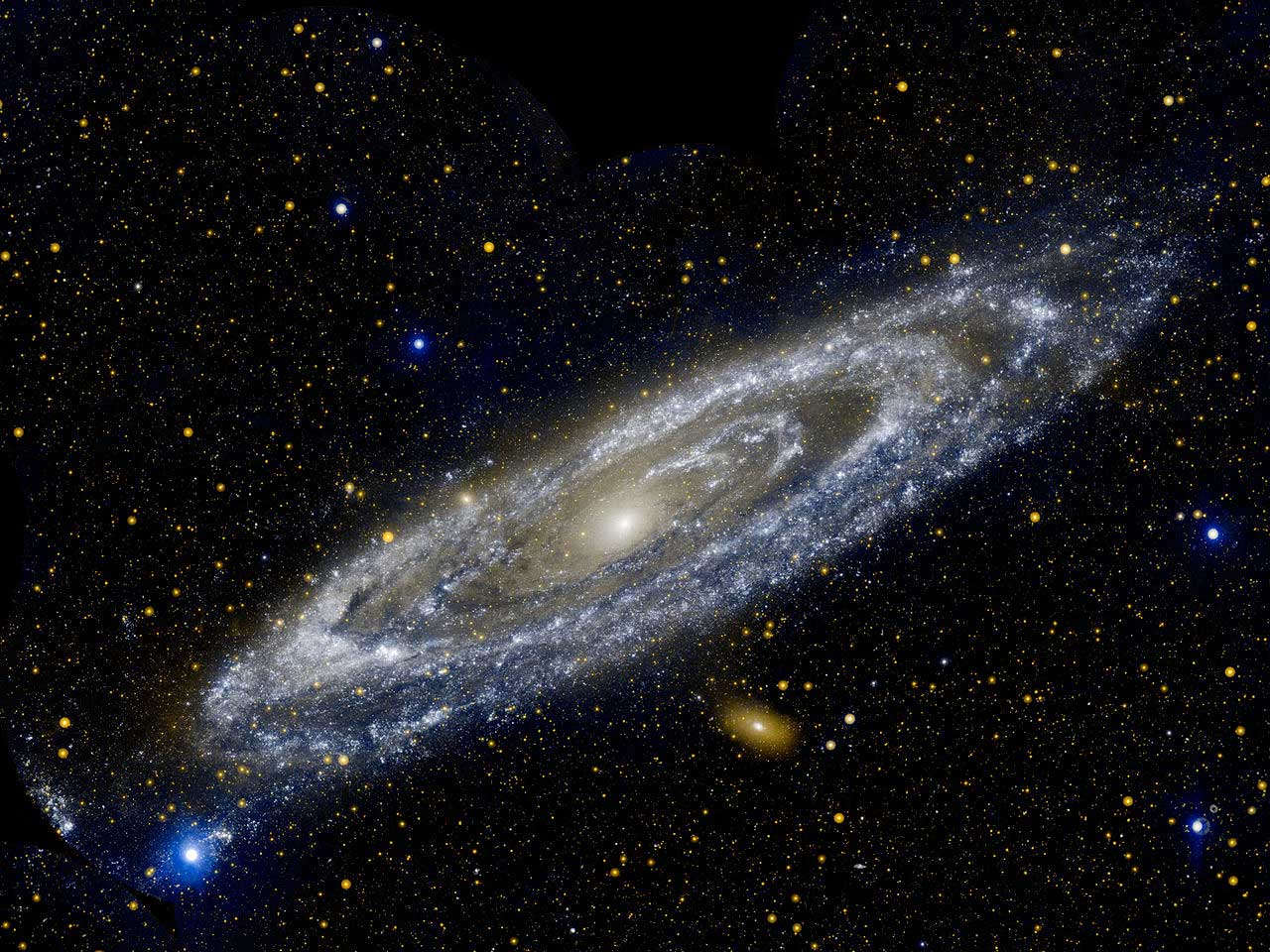

M31 - Andromeda
Closest major galaxy
2.5 million light-years
We have a meeting in about 4.5 billion years
Ellipticals
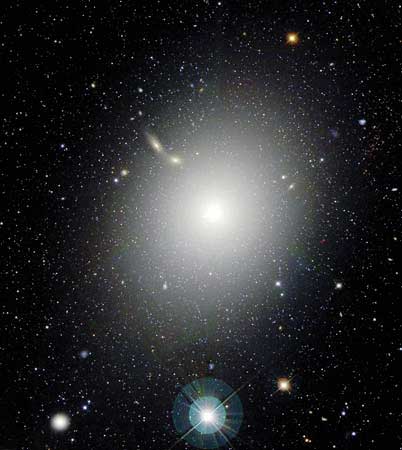

M87 Virgo a
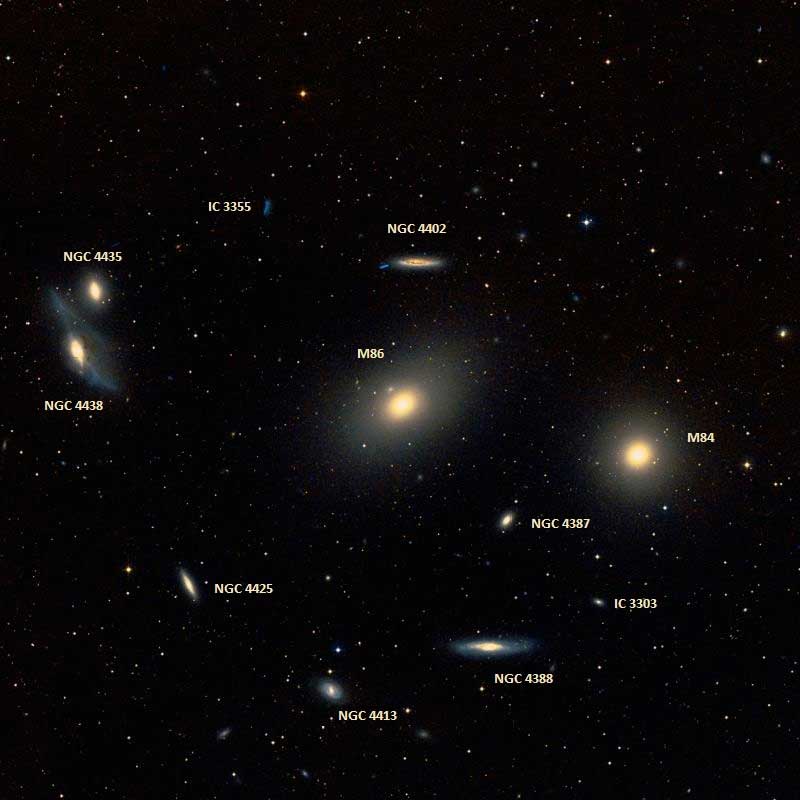

M84 and M86
Updates to the scheme
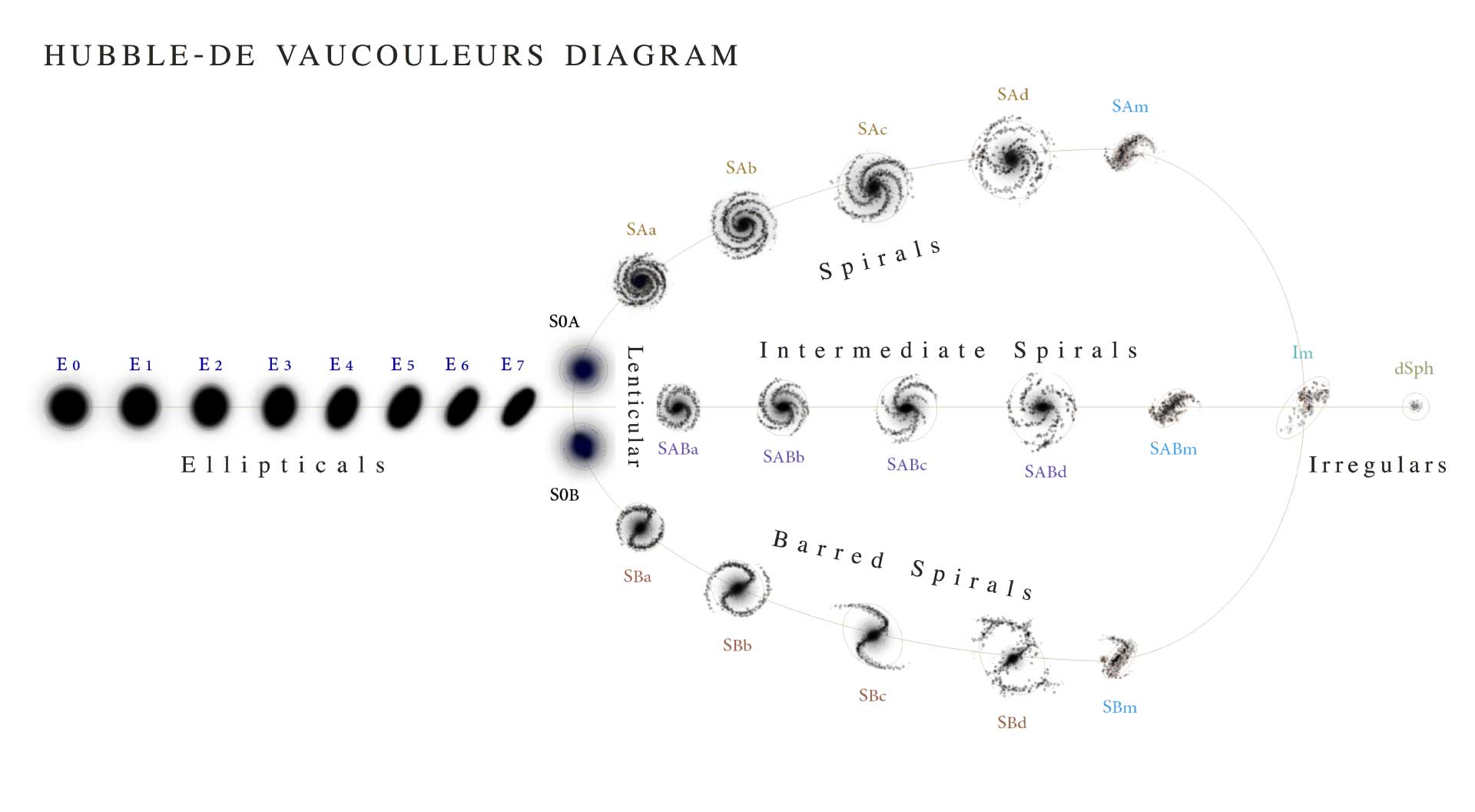
The Hubble - de Vaucouleurs system
By Antonio Ciccolella / M. De Leo - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Hubble-Vaucouleurs.png, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=50260841
NGC1300
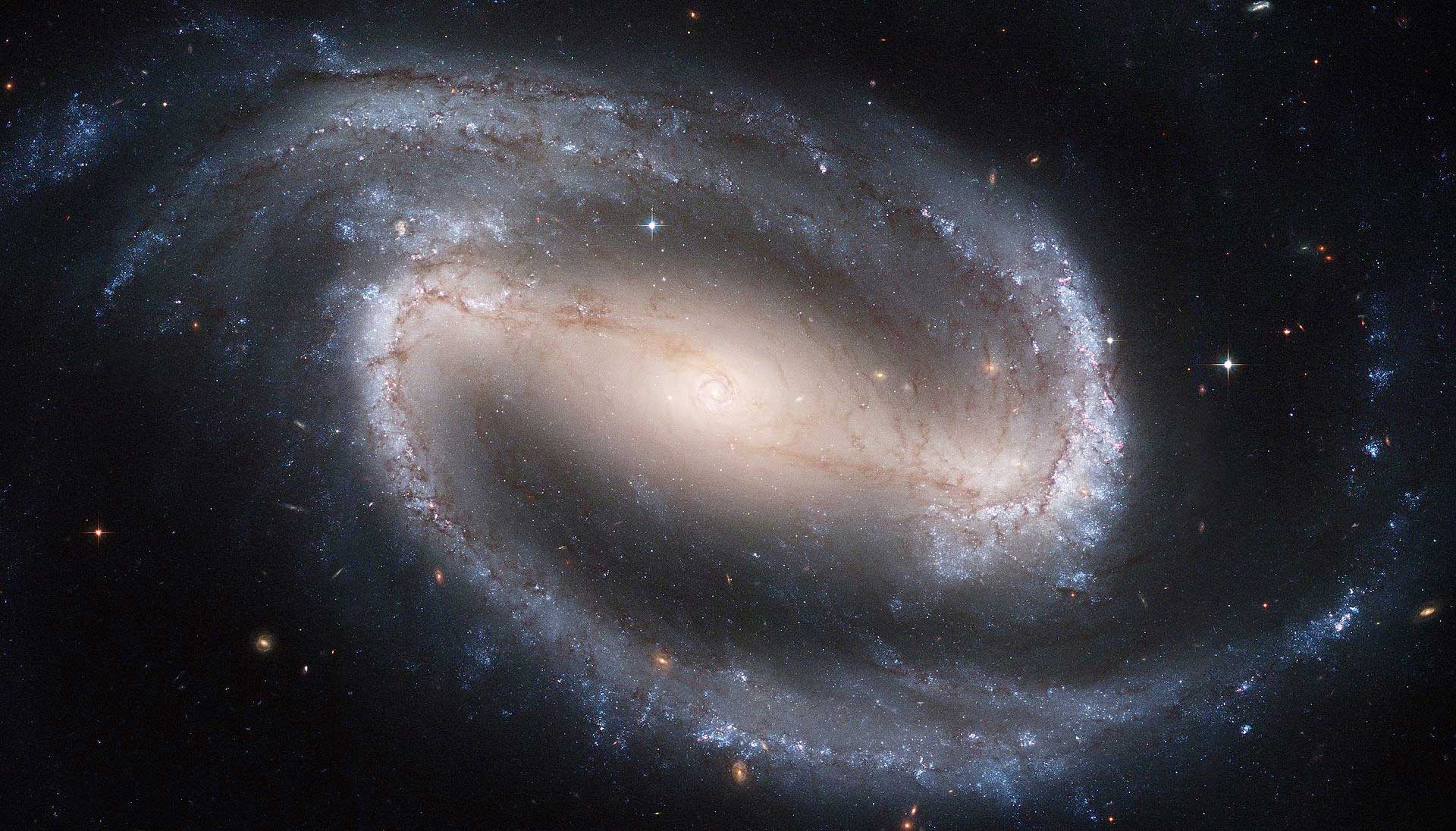

NGC1300 is an example of a barred galaxy.
By NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team STScI/AURA) - http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2005/01/image/ahttp://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo0501a/ ([cdn.spacetelescope.org/archives/images/screen/opo0501a.jpg direct link]), Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=119211
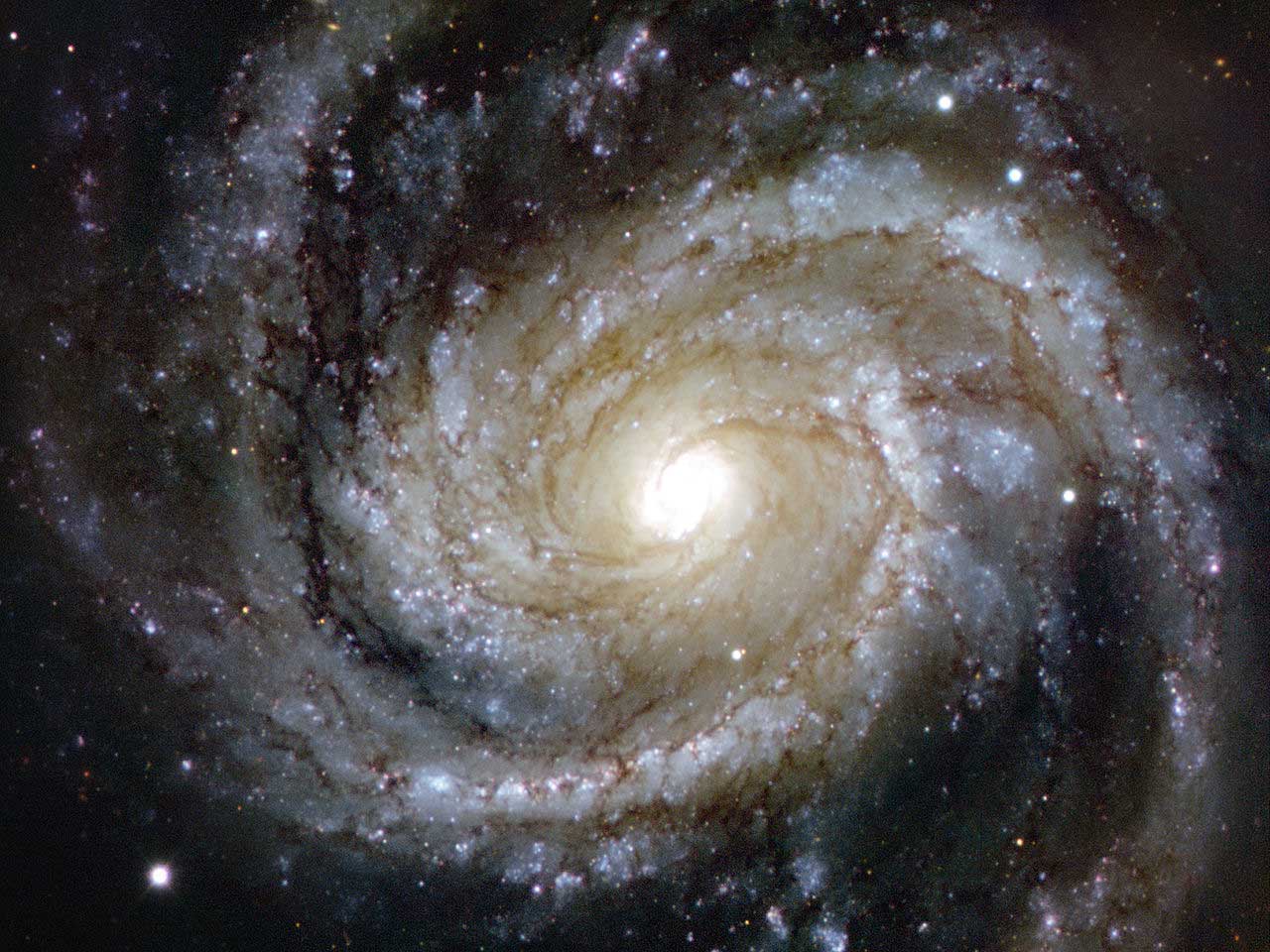

Messier 100 is a grand design spiral
Grand Design Spiral
A 'grand design' spiral has well defined arms.

The Whirlpool Galaxy (Spiral Galaxy M51, NGC 5194), a classic spiral galaxy located in the Canes Venatici constellation, and its companion NGC 5195.
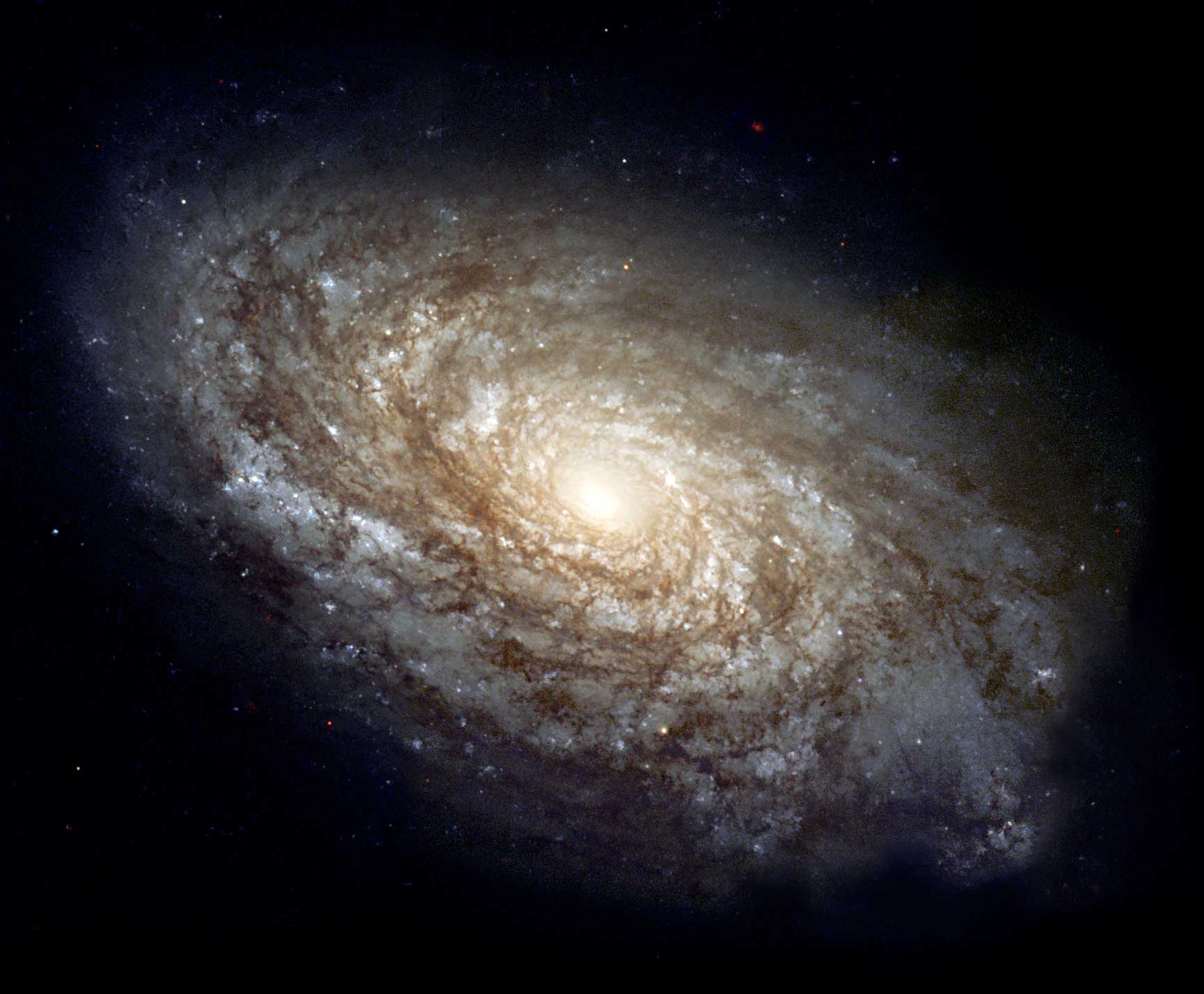

NGC_4414
Flocculent spiral galaxy
Flocculent ("having or resembling tufts of wool.") spirals don't have well defined arms
About 30% of spirals are like this.
- Disks: generally metal rich stars and ISM, nearly circular orbits with little random motion, spiral patterns
- Thin disks: younger, star forming, dynamically very cold
- Thick disks: older, passive, slower rotation and more random motions
- Bulge: metal poor to super-metal-rich stars, high stellar densities, mostly random motion – similar to ellipticals
- Bar: present in ~ 50 % of disk galaxies, mostly older stars, some random motions and a ~ solid body rotation?
- Nucleus: central (< 10pc) region of very high mass density, massive black hole or starburst or nuclear star cluster
- Stellar halo: very low density (few % of the total light), metal poor stars, globular clusters, low density hot gas, little or no rotation
- Dark halo: dominates mass (and gravitational potential) outside a few kpc, probably triaxial ellipsoids, radial profile ~ singular isothermal sphere, DM nature unknown
A largely successful classification scheme.
Although it was still rather qualitative based on just 'how they looked'.
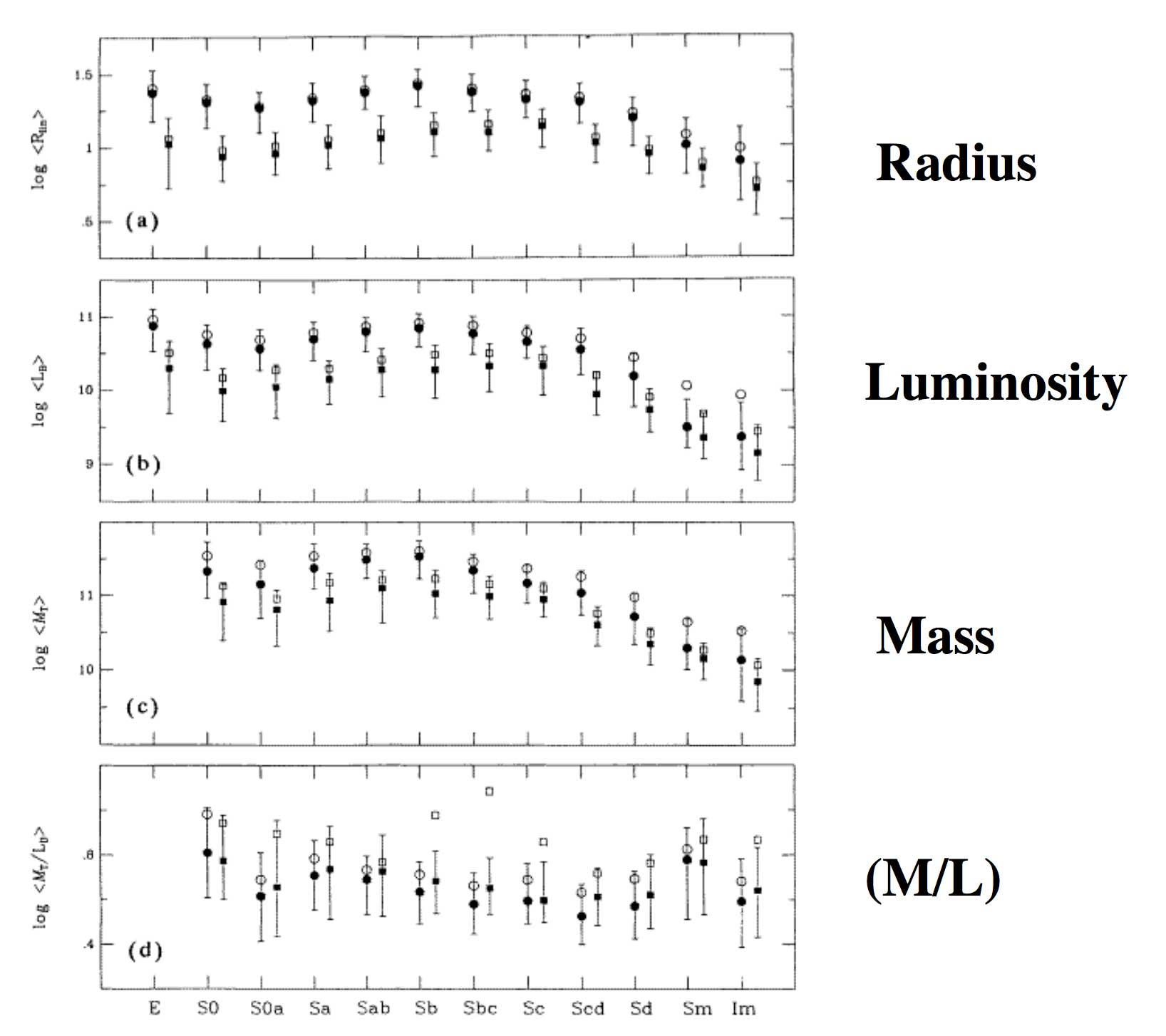
Some parameters don't correlate much with galaxy type.
M-81 in different wavelengths
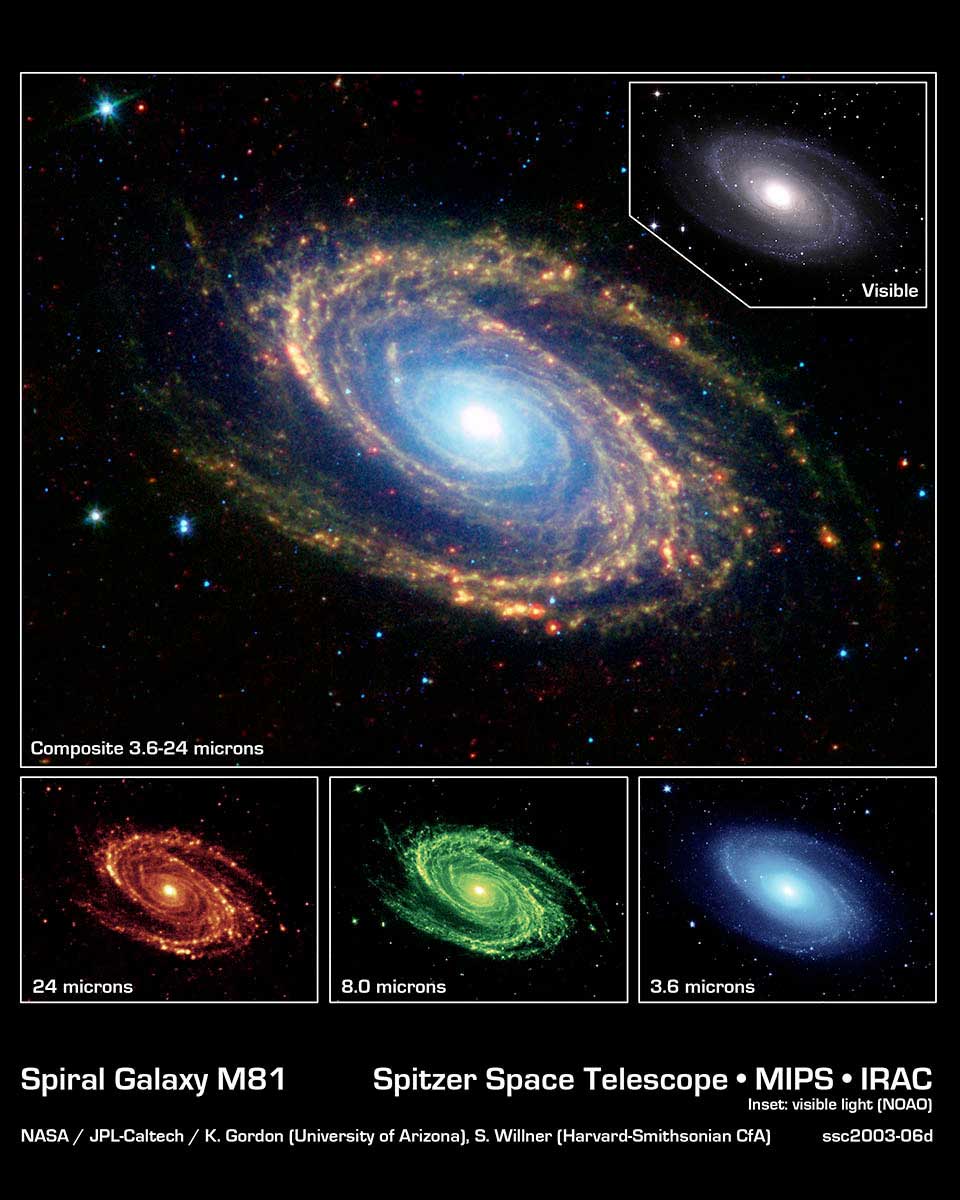
Messier Object 81 in different wavelengths
NASA/JPL-Caltech/K. Gordon (University of Arizona) & S. Willner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), N.A. Sharp (NOAO/AURA/NSF)
M81 in Multiple Wavelengths
Star formation
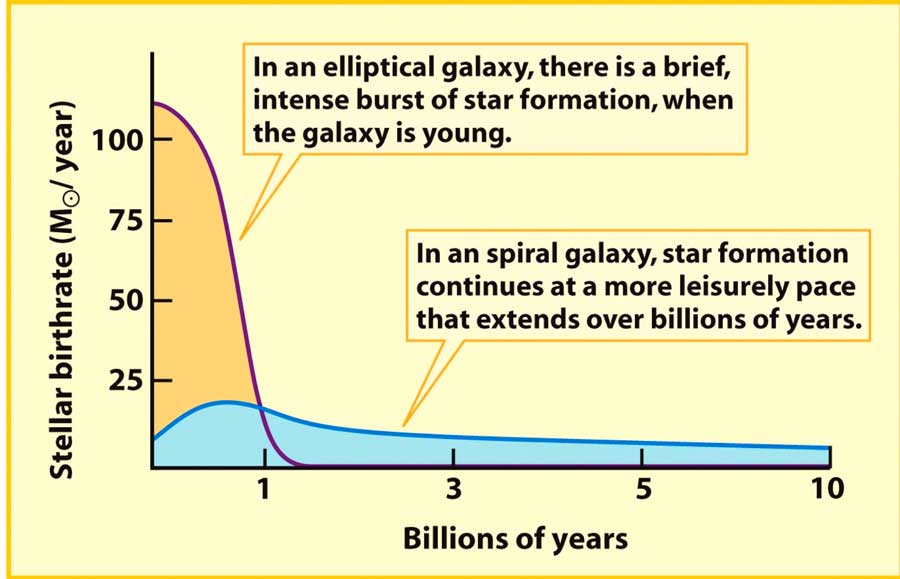
Ellipticals and early type spirals formed most of their stars early on (used up their gas, have older/redder stars)
Late type spirals have substantial on-going star-formation, didn’t form as many stars early-on (and thus lots of gas left)
Spiral Origins
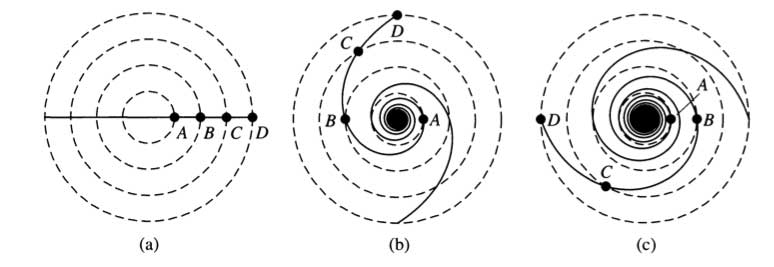
Stars closer to the center will take less time to go around. Over time, the arms will become 'tightly wound' and not observable spirals.
Density Wave Theory
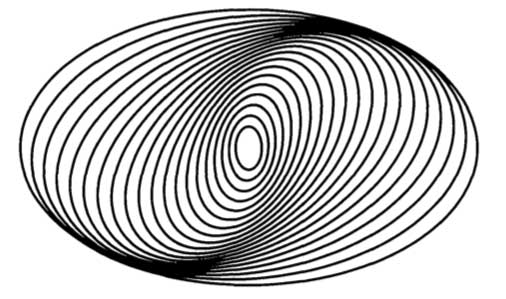
The orbits in the galaxy are elliptical, but slightly rotated. This causes regions of differing densities.
Higher density means higher gravitational force.
Objects (such as gas clouds) will be attracted to these regions and will drift towards them.
Spirals
Spiral arms are waves of compression that move around the galaxy and trigger star formation
Star formation will occur where the gas clouds are compressed
Simulations Here.
Ellipticals
Hubble originally thought there was not much going on elliptical galaxies. They just seems less complex.
Turns out that's not really the case. They are full of interesting features.
What's out there?
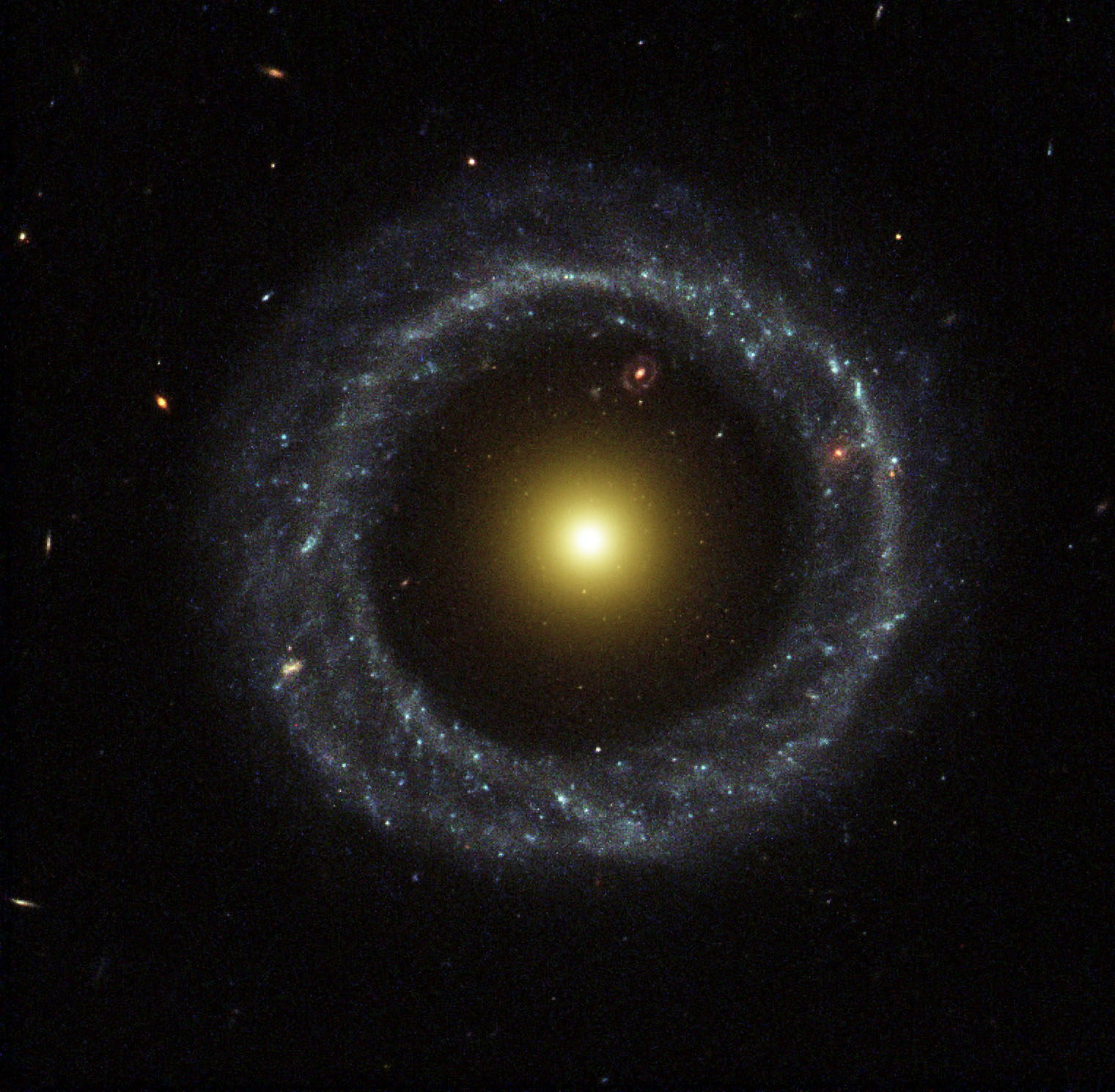

Hoag's object: a ring galaxy
By NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgment: Ray A. Lucas (STScI/AURA) - http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2002/21/image/a/http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap020909.html, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=610534
Other types:
- Rings
- Lenticular
- Irregulars
- Dwarf Galaxies
about 1011 galaxies in the visible universe - maybe more.
Over billions of years, galaxies interact.